biota
Type of resources
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
-

Reef Life Survey is a program that trains and assists a network of skilled and committed recreational divers to cost-effectively assess the state of the inshore marine environment at the continental scale. The program uses standardised underwater visual census methods employed by SCUBA divers to survey fish and invertebrate species and to record macroalgal and coral cover using photo quadrats - this record refers to the website for this program. By standardising techniques and establishing a monitoring system on a nation-wide scale, the program addresses many of the current problems associated with managing the marine environment, including the paucity, patchiness and variable quality of data on the distribution of and trends to marine biodiversity. A central database is managed for the storage, analysis and dissemination of data collected nationally, with a publicly-accessible web-based portal. The website allows information collected on Australia's marine environment to be accessed in a meaningful form by policy-makers and the general public, including recreational groups, scientists and industry. It also has information and resources for particpating divers and those wishing to become involved. The dataset generated by recreational divers will provide a national framework for monitoring the state of the inshore environment and the identification of those threats and locations of greatest conservation concern. This record points to the online resource for Reef Life Survey: http://www.reeflifesurvey.com/
-
Mesozooplankton community composition and structure were examined throughout the D’Entrecasteaux Channel, Huon Estuary and North West Bay, Tasmania, from November 2004 to October 2005, the data represented by this record was collected on the 17/08/2005. The composition of the mesozooplankton community was typical of inshore, temperate marine habitats, with seasonally higher abundance in summer and autumn and lower numbers in winter and spring. Copepods were the largest contributors to total abundance across all seasons and stations, while cladocerans and appendicularians were proportionally abundant in spring and summer. The faecal pellets of these three main groups, along with those of krill and amphipods, also contributed significantly to material recovered from sediment traps. Meroplanktonic larvae of benthic animals showed short-term peaks in abundance and were often absent from the water column for long periods. Spatially, North West Bay and the Channel had a higher representation of typically marine species, including Calanus australis and Labidocera cervi, while truly estuarine species, such as the copepod Gladioferens pectinatus, were more important in the Huon Estuary.
-
Mesozooplankton community composition and structure were examined throughout the D’Entrecasteaux Channel, Huon Estuary and North West Bay, Tasmania, from November 2004 to October 2005, the data represented by this record was collected on the 07/12/2004 The composition of the mesozooplankton community was typical of inshore, temperate marine habitats, with seasonally higher abundance in summer and autumn and lower numbers in winter and spring. Copepods were the largest contributors to total abundance across all seasons and stations, while cladocerans and appendicularians were proportionally abundant in spring and summer. The faecal pellets of these three main groups, along with those of krill and amphipods, also contributed significantly to material recovered from sediment traps. Meroplanktonic larvae of benthic animals showed short-term peaks in abundance and were often absent from the water column for long periods. Spatially, North West Bay and the Channel had a higher representation of typically marine species, including Calanus australis and Labidocera cervi, while truly estuarine species, such as the copepod Gladioferens pectinatus, were more important in the Huon Estuary.
-
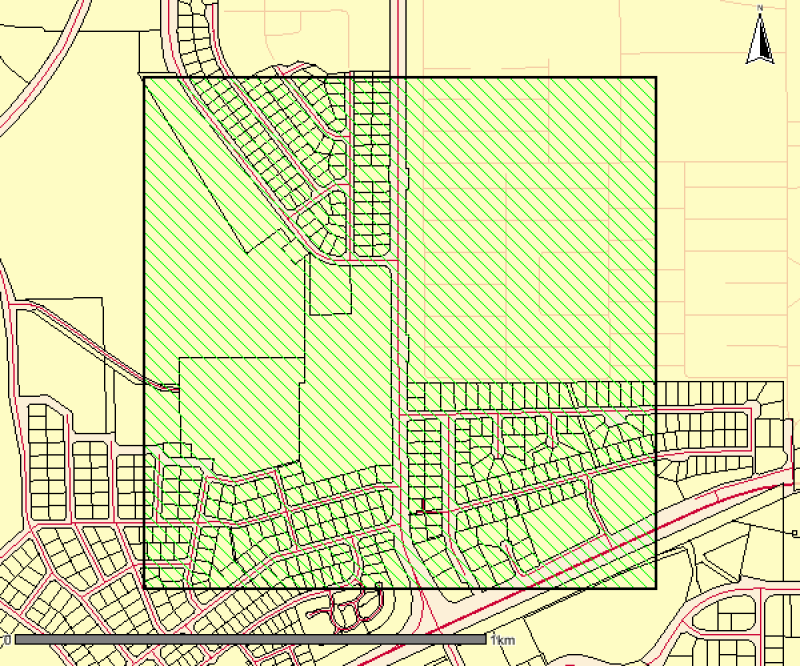
This is a high resolution survey (1:5,000 scale dataset) describing mapped vegetation communities for the Ludmilla Creek catchment area (within the City of Darwin, Northern Territory). (Vegetation Unit - A reasonably homogeneous part of the land surface, distinct from surrounding terrain with constant properties in landform and vegetation) This vegetation survey was undertaken in 1996. This dataset represents the vegetation on the ground at the time of the survey and reflects the data and methods used to create the mapped polygons. The dataset has been revised in 2015 to include community descriptions but has not been updated to reflect the vegetation on the ground. The Darwin Remnant Vegetation Survey is considered a more up-to-date representation of vegetation for this area.
-
Southern Rock Lobster (Jasus edwardsii) that are about to moult or have recently moulted have reduced market value due to higher mortality in live transport, higher cannibalism and lower meat recovery. Limiting the landing of softer shelled lobsters is desirable to maintain product quality. The effects of several factors on durometer readings were evaluated: sex, temperature (ambient plus elevated 3°C), location (from around the coast), and size (carapace length). Individuals were collected across two regions South Australia and Tasmania.
-
Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) are a keystone species in the Southern Ocean, but little is known about how they will respond to climate change. Ocean acidification, caused by sequestration of carbon dioxide into ocean surface waters (pCO2), is known to alter the lipid biochemistry of some organisms. This can have cascading effects up the food chain. In a year-long laboratory experiment adult krill were exposed to ambient seawater pCO2 levels (400 μatm), elevated pCO2 levels that mimicked near-future ocean acidification (1000, 1500 and 2000 μatm) and an extreme pCO2 level (4000 μatm). The laboratory light regime mimicked the seasonal Southern Ocean photoperiod and krill received a constant food supply. Total lipid mass (mg g -1 DM) of adult krill was unaffected by near-future levels of seawater pCO2. Fatty acid composition (%) and fatty acid ratios associated with immune responses and cell membrane fluidity were also unaffected by near-future pCO2, apart from an increase in 18:3n-3/18:2n-6 ratios in krill in 1500 μatm pCO2 in winter and spring. Extreme pCO2 had no effect on krill lipid biochemistry during summer. During winter and spring, krill in extreme pCO2 had elevated levels of omega-6 fatty acids (up to 1.2% increase in 18:2n-6, up to 0.8% increase in 20:4n-6 and lower 18:3n-3/18:2n-6 and 20:5n-3/20:4n-6 ratios), and showed evidence of increased membrane fluidity (up to three-fold increase in phospholipid/sterol ratios). These results indicate that the lipid biochemistry of adult krill is robust to near-future ocean acidification.
-

Surveying habitats critical to the survival of grey nurse sharks in South-East Queensland has mapped critical habitats, gathered species inventories and developed protocols for ecological monitoring of critical habitats in southern Queensland. This information has assisted stakeholders with habitat definition and effective management. In 2002 members of UniDive applied successfully for World Wide Fund for Nature, Threatened Species Network funds to map the critical Grey Nurse Shark Habitats in south east Queensland. UniDive members used the funding to survey, from the boats of local dive operators, Wolf Rock at Double Island Point, Gotham, Cherub's Cave, Henderson's Rock and China Wall at North Moreton and Flat Rock at Point Look Out during 2002 and 2003. These sites are situated along the south east Queensland coast and are known to be key Grey Nurse Shark aggregation sites. During the project UniDive members were trained in mapping and survey techniques that include identification of fish, invertebrates and substrate types. Training was conducted by experts from the University of Queensland (Centre of Marine Studies, Biophysical Remote Sensing) and the Queensland Parks and Wildlife Service who are also UniDive members. The monitoring methods (see methods) are based upon results of the UniDive Coastcare project from 2002, the international established Reef Check program and research conducted by Biophysical Remote Sensing and the Centre of Marine Studies. This record describes the digitised habitat features for Wolf Rock. View the original metadata record at https://doi.pangaea.de/10.1594/PANGAEA.864211 for the full data collection.
-
Aquatic flora surveys were conducted in Wilson Inlet in 2007 and 2008. This data is part of the 2013 report "Synthesis of seagrass mapping studies" conducted by the Water Science Branch of the Department of Water. The 2007 survey was conducted to review any changes in seagrass distribution since the previous survey in 1996 (data not included in this record), and was funded internally by the Water Science branch. The 2008 survey was conducted by the WA Department of Water together with Geoscience Australia. The objective of the 2008 survey was to collect baseline data on seagrass composition and distribution in key estuaries of southern and south-western WA. This data was acquired by the ACEAS Seagrass Group as part of the 2013 Australia-wide risk assessment of Seagrass. Surveys were conducted again in December 2017, April 2018, December 2019, December 2020, December 2021 and December 2022 by the Department of Water and Environmental Regulation as "Wilson Inlet Seagrass Survey". The datasets making up the 2007-2008 Wilson Inlet seagrass survey data are: WA_WilsonInlet_seagrass_polygons - polygon dataset showing interpolated percentage cover of seagrass with species information (where available). This record provides access to the initial WA DoW surveys. See associated DWER records in Data WA catalogue for access to newer surveys at this site.
-

This record describes an aggregated data product compiled from a number of different surveys of Macrocystis surface cover in Tasmanian waters, spanning 1950 to 2019. Some surveys represent a statewide census of Macrocystis cover, while others are targeted surveys of smaller regions. Methodology and data quality may also vary between surveys. Please see linked metadata records for specific methodologies and quality statements applying to individual surveys.
-
This project used marine benthic imagery and fine-scale oceanographic data to refine existing models of the contemporary circumpolar distribution of Antarctic benthic biodiversity, and used oceanographic models developed in the ACEAS program to generate spatial predictions of the distribution of various aspects on benthic biodiversity and blue carbon under future climate scenarios. ***Access to data is currently embargoed, to be made available ~June 2026***
 IMAS Metadata Catalogue
IMAS Metadata Catalogue