2022
Type of resources
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
-

Seagrass meadow extent and meadow-scape was mapped using four alternative approaches at Yule Point, a coastal clear water habitat, in the Cairns section of the Great Barrier Reef, between October 2017 and July 2020. Approach 1 included mapping meadow boundaries and meadow-scape during low spring tides on foot using a handheld GPS. Approach 2 was where the meadows were surveyed at low tide with observations from a helicopter, with observational spot-checks conducted at a number haphazardly scattered points. Approach 3 used imagery collected during low spring tides with a UAV at an altitude of 30 m with a resolution of 0.2cm/pixel. Approach 4 used PlanetScope Dove imagery captured on 05 September 2017 and 09 August 2019 coinciding as close as possible to the field-surveys in 2017 and 2019, with 3.7 m x 3.7 m pixels (nadir viewing) acquired from the PlanetScope archive. This record describes meadow extent data collected using Approach 4 (PlanetScope imagery). View the original metadata record at https://doi.pangaea.de/10.1594/PANGAEA.946604 for the full data collection.
-

This Resource is a maps of Australian Maritime Safety Authority (AMSA) Shipping waste and oil spills for current, 2013-2017 and 2018-2023.
-

This record provides an overview of the NESP Marine and Coastal Hub project "Aerial survey of the Southern Right Whale ‘western’ sub-population off southern Australia". For specific data outputs from this project, please see child records associated with this metadata. -------------------- Southern right whales are listed as Endangered under the EPBC Act and are a species of national conservation significance. Monitoring of their recovery is guided by the Southern Right Whale Conservation Management Plan, which aims to improve the population’s conservation status through regular assessment of population size, calving intervals, and spatial trends. This project continued the long-term aerial survey program of southern right whales along the southern Australian coast, spanning from Perth (WA) to Ceduna (SA). Annual surveys have been conducted since 1993, providing a continuous long-term dataset for the 'western' population and supporting national assessments of connectivity with the smaller ‘eastern’ population. The surveys contribute essential data on population trends, calving rates, and movements of individuals. The August 2022 aerial survey ensured an uninterrupted time series in the long-term population trend data. This is particularly important given the species' non-annual breeding cycle (typically every three years). Annual surveys are essential to maintain an acceptable level of precision in estimating population trends and key life history parameters. A total of 526 whales were recorded, including 247 cow–calf pairs, 31 unaccompanied adults and one yearling. Based on long-term models, this equated to a population estimate of approximately 2,675 individuals, with an average annual growth rate of ~5.3%. While this represents a continued population growth, results suggest a possible slowing in the rate of growth over the past 13 years (from 7.5% in 2009). The 2022 survey also recorded the lowest number of unaccompanied animals in the entire time series, extending a five-year trend of low sightings in this group. Continued monitoring of the population is needed to assess whether these changes represent longer-term shifts in population dynamics and calving intervals, and to inform adaptive management for this long-lived, slow-recovering species. Outputs • Estimate of relative abundance and population trend compared to long-term aerial survey sightings [dataset] • Individual whale photo-identification data - 2021-22 season [imagery - published to ARWPIC] • Final technical report detailing overall numbers of southern right whales observed within the survey region, their gender (and life stage where possible) and spatial distribution of individuals [written]
-
This data is from the 2021 'Seeds for Snapper' season which is a community volunteer seed based seagrass restoration program located in Perth, Western Australia. It details the effort that went into the collection of Posidonia australis seagrass fruit including number of divers, number of shore support personnel, volunteered hours, and fruit collection metrics (volume, estimated number).
-
Dive surveys were conducted in 2014 and the same sites resurveyed annually until 2022 (excluding 2021), to establish a baseline and monitor the status of the critically endangered spotted handfish (Brachionichthys hirsutus) population. This dataset is a summary of all surveys season 2014 to 2022 (excluding 2021) in which the 11 sites across the Derwent Estuary and D'Entrecasteaux Channel were assessed. The data describes the search effort (transect length, swathed area) and counts of handfish observed on each transect, including size measurements (total length) and depth records for each sighted fish.
-
Collection of processed BGC-Argo float profiles, used to calculate phytoplankton phenology from chlorophyll, phytoplankton carbon and nitrate.
-
This record described kelp growth and ecophysiological data relevant to the thermal tolerance of specific warm-tolerant and 'normal' family-lines of giant kelp (Macrocystis pyrifera) from Tasmania, Australia. Australia’s giant kelp forests are listed as a Threatened Ecological Community under the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999. Habitat restoration is a potential tool for the conservation and management of giant kelp ecosystems. For habitat restoration to be effective, the cause of habitat decline must be understood and overcome. This is problematic when climate change is driving habitat loss since it cannot be reversed or ameliorated prior to restoration. A previous NESP project led by this team (Project E7, Marine Biodiversity Hub) identified warm-tolerant strains of giant kelp from remnant patches in eastern Tasmania, where the species has experienced precipitous declines due to ocean-warming. These strains have high potential to assist with ‘future-proofing’ kelp forest restoration, however it is still unclear what the physiological mechanisms are that provide their improved thermal tolerance. This work cultivated the warm-tolerant strains of giant kelp previously identified, along with giant kelp strains of normal tolerance, at both cool (16 °C) and warm temperatures (20 °C). The juvenile kelp was then harvested, and a suite of physiological traits that may be responsible for their differences in thermal tolerance were examined. These included nutrient usage (carbon and nitrogen content), cellular membrane processes (fatty acid contents), and photosynthesis (PAM fluorometry and photosynthetic pigments). The cultivation trials again illustrated the improved ability of the warm-tolerant strains to develop at stressful warm temperatures relative to normal giant kelp. This work demonstrated for their first time that the improved thermal performance of these strains may extend to the development and fertilisation of the earlier kelp ‘gametophyte’ life-stage. Despite the clear differences in growth between the two test groups, the physiological assessments illustrated a complex pattern of responses, some of which are contrary to expected based on prior knowledge of thermal performance in kelps. Nonetheless, these results indicate that the warm-tolerant strains of giant kelp have a greater capacity to alter the composition of their fatty acids and may be more efficient users of nitrogen (a key nutrient for growth and development). This new information will help inform ongoing kelp breeding and selection programs for future-proofing kelp restoration in Australia and globally. The improved understanding of the physiology of kelp thermal tolerance might also help with identifying individuals and populations of Macrocystis, and other kelps, that may be resilient to (or especially threatened by) ocean warming and climate change.
-
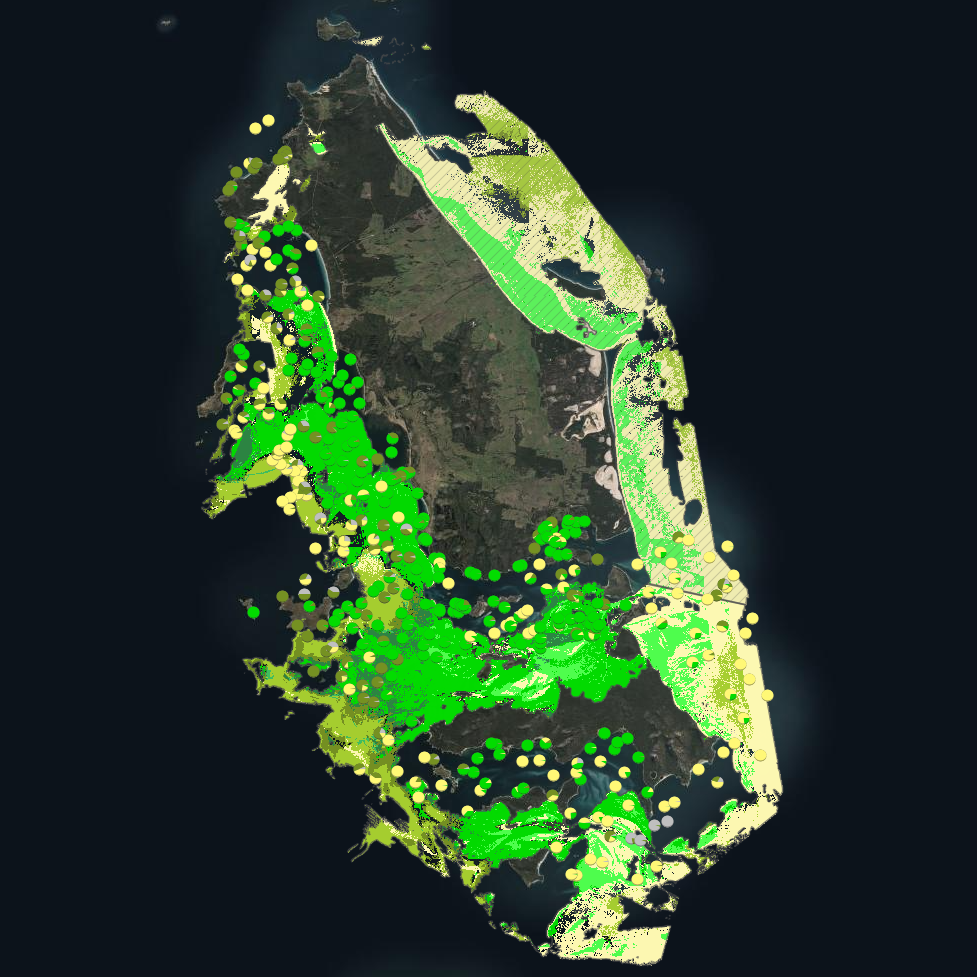
***This record contains a subset of benthic habitat data from https://doi.org/10.25959/E4S6-GE74 (NESP MaC Project 3.6) rehosted for the purposes of the Seamap Australia collaborative project.*** Seagrass beds are a dominant marine ecosystem of Tayaritja (the Furneaux Group of Islands) in the north-eastern waters off Tasmania. Historical coarse mapping has indicated extensive beds of Posidonia, Amphibolis, Heterozostera, and Zostera species, potentially comprising some of the largest and deepest seagrass extents found in temperate Australian waters. However, limited data on the distribution and ecological value of these seagrass habitats represents a significant knowledge gap in understanding Australia's wetland natural assets. This project mapped the extent, ecological composition, population structure, and blue carbon value of seagrass beds around Tayaritja, in partnership with the Tasmanian Aboriginal Centre, as part of NESP Marine and Coastal Hub Project 3.6. The study area focused on the coastal waters surrounding Flinders Island in the western Furneaux Group, with mapping extending from the high tide line to the depth limit of reliable optical detection (approximately 30 m), based on analysis of field data and satellite imagery capabilities in the region. This metadata record specifically describes the benthic mapping component of the study. A combination of close-range remote sensing methods was used to map the extent and ecological values of seagrass beds. High-resolution satellite imagery from Sentinel-2 (10 m) sensors, combined with bathymetric LiDAR data and oceanographic variables, was used to map baseline seagrass extent and composition. A field campaign deployed a Benthic Observation Survey System (BOSS) and unBaited Remote Underwater stereo-Video system (stereo-uBRUV) at approximately 400 locations to validate remote sensing outputs, collecting field photo quadrats and rhizome cores. From these data, maps were produced showing the extent and coverage of seagrass, sand, and macroalgae, and where possible, seagrass species composition, subject to water depth and clarity constraints. See the "Lineage" section of this record for full methodology.
-

Seagrass meadow extent and meadow-scape was mapped using three alternative approaches at Midge Point, a coastal turbid water habitat, in the central section of the Great Barrier Reef, in September/October 2017. Approach 1 included mapping meadow boundaries and meadow-scape during low spring tides on foot using a handheld Garmin GPS. Approach 2 was where the meadows were surveyed at low tide with observations from a helicopter, with observational spot-checks conducted at a number haphazardly scattered points. Approach 3 used PlanetScope Dove imagery captured on 09 October 2017 coinciding as close as possible to the field-surveys, with 3.7 m x 3.7 m pixels (nadir viewing) acquired from the PlanetScope archive. This record describes meadow extent data collected using Approach 3 (PlanetScope imagery). View the original metadata record at https://doi.org/10.1594/PANGAEA.946606 for the full data collection.
-

Seagrass meadow extent and meadow-scape was mapped using two alternative approaches at Green Island, a reef clear water habitat, in the Cairns section of the Great Barrier Reef, in November 2020. Approach 1 included mapping seagrass meadow-scape using imagery captured during low spring tides with a DJI Mavic 2 Pro UAV at an altitude of 100 m, with a resolution of 2.45cm/pixel. Approach 2 used PlanetScope Dove imagery captured on 05 November 2020 coinciding as close as possible to the field-surveys from 25 to 27 November 2020, with 3.7 m x 3.7 m pixels (nadir viewing) acquired from the PlanetScope archive. This record describes meadow extent data collected using Approach 2 (PlanetScope imagery). View the original metadata record at https://doi.pangaea.de/10.1594/PANGAEA.946605 for the full data collection.
 IMAS Metadata Catalogue
IMAS Metadata Catalogue