EARTH SCIENCE | BIOSPHERE | ECOSYSTEMS | MARINE ECOSYSTEMS | BENTHIC
Type of resources
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
-
This project updates the 2019 predictive benthic habitat map for this region, extending past the subtidal zone of the harbour to include intertidal habitats. The project worked with collaborators to synthesise existing data sets for inclusion in benthic habitat mapping process. Hydrodynamic model variables were updated and new digital elevation data included to provide a more accurate representation of the bed shear stress, waves and current. LiDAR surveys were conducted to fill in the gap between the IX bathymetric survey and the high tide water mark. The LiDAR survey data extended the existing bathymetry data. A total of 30 towed video transects were conducted in areas predicted to have a high probability of benthic fauna occurrence based on the existing predictive model. The benthic habitat model was updated to include NTG historical data, new towed video data, hydrodynamic and light data.
-
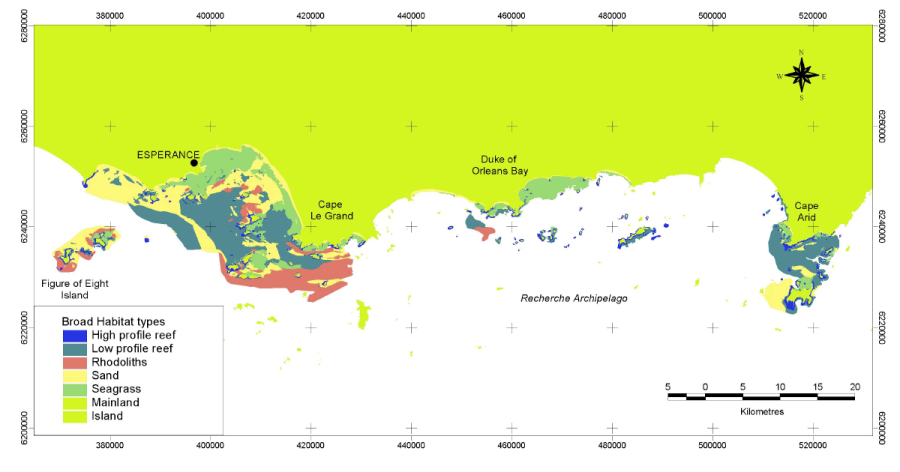
The Fisheries Research and Development Corporation Project (FRDC) No. 2001/060 characterised and identified the distribution of the different benthic habitats of the Recherche Archipelago and identified the distribution of assemblages of fish, mobile invertebrates, filter feeding communities and seagrasses and the patterns and processes which structure them. Benthic habitat were determined from the interpretation of Landsat imagery, sidescan sonar imagery and video validation data collected within the Recherche region from May 2002 to November 2003.
-
The goal of the program was developing comprehensive inventories and maps of the distribution and abundance of physical and biological seabed habitats, seagrasses and benthic assemblages to provide baseline environmental mapping and a description of ecological patterns. The benthic habitat mapping was performed by utilising R/Python and Maxent software within the species distribution modelling domain. We correlated the probability of occurrence of individual benthic habitat classes with the environmental predictors developed form the multibeam hydroacoustic dataset. The data is presented as a maximum likelihood map incorporating all five prediction classes: (1- Macroalgae; 2- Filter Feeders; 3- Seagrass; 4- Hard Corals; 5- Bare seafloor). An updated version of this data are available (2022) Revised predictive benthic habitat map for Darwin Harbour. Report prepared for Department of Environment, Parks and Water Security. Australian Institute of Marine Science, Darwin, 127 pp.
-
The CSIRO’s Oceans & Atmosphere Shallow Survey Internal Facility (SSIF) was contracted by the Institute for Marine and Antarctic Studies (IMAS) of the University of Tasmania (UTAS) in collaboration with Parks Australia, to undertake a hydrographic survey of the Boags Commonwealth Marine Reserve in the southwestern Bass Strait. This site was surveyed in conjunction with other smaller sites for Petuna Aquaculture, as part of a broader survey campaign. All of the sites covered in this campaign are located in the vicinity of the Hunter Group of Islands, off the north-western coast of Tasmania.
-
Assessment of Posidonia australis transplant survival at 3, 8, 12, 18, and 26 months (August transplant); and 3, 8, 12, 18, 26 and 30 months (April transplant), after planting at Middle Bluff, and Dubaut Point, Shark Bay.
-
Sediment organic carbon assessments within plots of transplanted Posidonia australis seagrass, and compared to adjacent bare sand and healthy meadows, in Shark Bay, WA.
-
Growth (shoot count) of Amphibolis antarctica and Posidonia australis following transplant to Middle Bluff and Dubaut Point, Shark Bay. Plants were transplanted by the Malgana people with assistance from UWA staff then assessed for shoot counts after 8 months.
-
We performed a 5-week experiment in controlled laboratory settings to investigate the effects of different types of microparticles (i.e., PVC/red clay) on the performance of the Mediterranean mussel. Several response variables including respiration rate, byssus production, body condition index and survival were collected. Our study's main purpose is to examine effects of synthetic microparticles on bivalves using a more relevant methodological approach, i.e., in comparison to naturally-occurring particles, since these filter-feeders are exposed to not just microplastics in the real-world environment, but also to various naturally suspended seston particles, such as detritus and sediments.
-
The Tasman Fracture Commonwealth Reserve complements the Port Davey Marine Reserve (encompassing Port Davey, Bathurst Channel and Bathurst Harbour), which was proclaimed by the Tasmanian Government in 2005. It spans the continental shelf, continental slope and deeper water ecosystems south of Tasmania, and is scored by steep canyons. It also encloses other geological features, including steep escarpments and troughs, saddles, basins, and part of a plateau that is over 400 km long and rises up to 3 km above the sea floor. The reserve includes a number of undersea peaks rising to less than 1500 m below the sea surface that provide habitat to deepwater hard corals. These corals provide a structure and habitat for a rich diversity of marine invertebrate animals that live attached corals. This record describes a geomorphology map for the Tasman Fracture CMR that was prepared using bathymetry and backscatter data sourced from CSIRO and Geoscience Australia.
-
Biodiversity assessments of invertebrates within seagrass (Amphibolis antarctica and Posidonia australis) transplant plots, compared to adjacent bare sand and healthy meadows at Middle Bluff, Dubaut Point and Useless Loop, Shark Bay.
 IMAS Metadata Catalogue
IMAS Metadata Catalogue