National Environmental Science Program (NESP) Marine and Coastal Hub
Type of resources
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
-
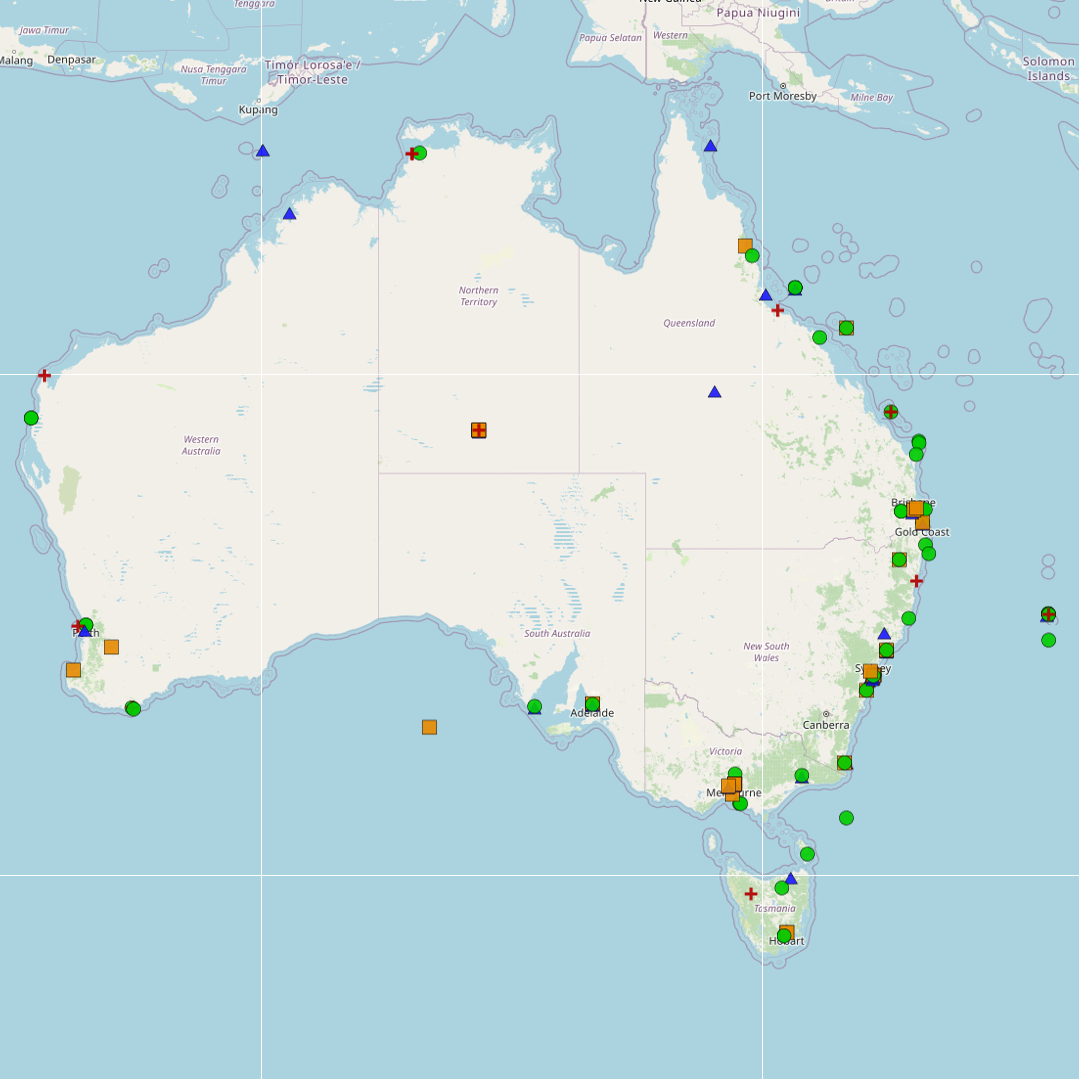
A review of peer-reviewed publications was undertaken, focusing on coastal and marine microplastics relevant to South Eastern Australia (South Australia, Victoria, and New South Wales), as well as from ongoing citizen science programmes from AUSMAP (https://www.ausmap.org/). This dataset summarises basic information about the microplastics studies: the location of the study; if the study focused on water, sediment or biota; the type of biota (for biotic studies); and the DOI of the publication. Although the primary focus of this study was restricted to southeastern Australia, studies collated from other regions have also been included in this dataset. The outcomes of the literature review for other regions (QLD, NT, SA, WA, Tas) should not be considered comprehensive.
-

This metadata record provides a brief overview of the National Environmental Science Program (NESP) Marine and Coastal (MaC) Hub. The record acts as an aggregation point for all NESP Marine and Coastal Hub data collections and projects developed as part of this research program. The National Environmental Science Program (NESP) is a long-term commitment by the Australian Government to environment and climate research. The first phase invested $145 million (2014-15 to 2020-21) into 6 research hubs. The second phase invests $149 million (2020-21 to 2026-27) into 4 new research hubs. The program builds on its predecessors – the National Environmental Research Program (NERP) and the Australian Climate Change Science Programme (ACCSP) – to support decision-makers to understand, manage and conserve Australia’s environment by funding world-class biodiversity and climate science. The Marine and Coastal Hub is a collaborative partnership supported by funding from the Australian Government administered by the Department of Climate Change, the Environment, Energy and Water (DCCEEW) - previously Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment (DAWE). The current NESP funding program runs from 2021 to 2027. The Marine and Coastal Hub is co-administered by the University of Tasmania (UTAS), and the Reef and Rainforest Research Centre (RRRC). The Marine and Coastal Hub delivers: • applied research to support management of Australia’s marine and coastal environments including estuaries, coast, reefs, shelf and deep-water • targeted biodiversity and taxonomy products to support efficient system monitoring • environmental monitoring systems and decision-support tools. Research products from the NESP Marine and Coastal Hub are available from https://nespmarinecoastal.edu.au and the Australian Ocean Data Network catalogue (http://catalogue.aodn.org.au)
-

This record provides an overview of the NESP Marine and Coastal Hub small-scale study - "Towards a consolidated and open-science framework for restoration monitoring". No data outputs were generated by this project. -------------------- Coastal habitat restoration is scaling up rapidly in Australia and covers a range of diverse ecosystems including oyster reefs, seagrass meadows, mangrove forests, kelp forests, and saltmarshes. While monitoring is commonly included in these projects, approaches are often uncoordinated, inconsistently funded, and rarely follow open science protocols. Previous NESP-funded projects have advanced understanding of the ecology and service provision of threatened ecosystems and established targets for repair based on reference conditions (e.g. Marine Biodiversity Hub project B4). They also created a national database of marine and coastal restoration projects (Australian Coastal Restoration Network: project E5) and supported the development of monitoring, evaluation, reporting and improvement (MERI) systems across various sectors. Building on this foundation, the current project synthesised monitoring approaches across multiple habitat types by drawing on the collective expertise of Australian researchers. It also explored the integration of emerging technologies—such as automation, artificial intelligence, and eDNA—to improve monitoring efficiency and cost-effectiveness. The primary output of this project is a coordinated, open-science monitoring framework that incorporates clearly defined restoration goals and a core set of universal variables. Developed through expert consultation, the framework supports consistent benchmarking across projects while accommodating habitat-specific and goal-driven metrics. The framework promotes data accessibility, standardised definitions, and the integration of new technologies to streamline the development of future restoration projects and maximise the value of restoration monitoring. Outputs • Best-practice toolkit / final project report [written]
-
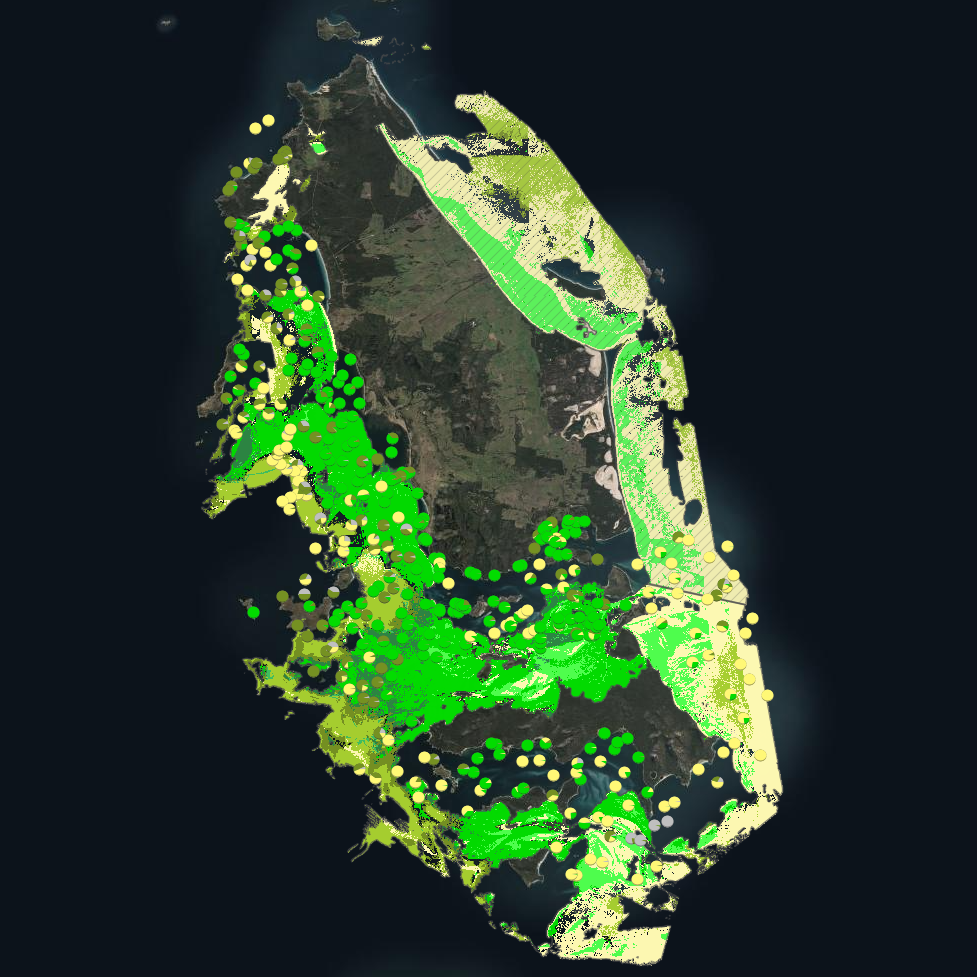
***This record contains a subset of benthic habitat data from https://doi.org/10.25959/E4S6-GE74 (NESP MaC Project 3.6) rehosted for the purposes of the Seamap Australia collaborative project.*** Seagrass beds are a dominant marine ecosystem of Tayaritja (the Furneaux Group of Islands) in the north-eastern waters off Tasmania. Historical coarse mapping has indicated extensive beds of Posidonia, Amphibolis, Heterozostera, and Zostera species, potentially comprising some of the largest and deepest seagrass extents found in temperate Australian waters. However, limited data on the distribution and ecological value of these seagrass habitats represents a significant knowledge gap in understanding Australia's wetland natural assets. This project mapped the extent, ecological composition, population structure, and blue carbon value of seagrass beds around Tayaritja, in partnership with the Tasmanian Aboriginal Centre, as part of NESP Marine and Coastal Hub Project 3.6. The study area focused on the coastal waters surrounding Flinders Island in the western Furneaux Group, with mapping extending from the high tide line to the depth limit of reliable optical detection (approximately 30 m), based on analysis of field data and satellite imagery capabilities in the region. This metadata record specifically describes the benthic mapping component of the study. A combination of close-range remote sensing methods was used to map the extent and ecological values of seagrass beds. High-resolution satellite imagery from Sentinel-2 (10 m) sensors, combined with bathymetric LiDAR data and oceanographic variables, was used to map baseline seagrass extent and composition. A field campaign deployed a Benthic Observation Survey System (BOSS) and unBaited Remote Underwater stereo-Video system (stereo-uBRUV) at approximately 400 locations to validate remote sensing outputs, collecting field photo quadrats and rhizome cores. From these data, maps were produced showing the extent and coverage of seagrass, sand, and macroalgae, and where possible, seagrass species composition, subject to water depth and clarity constraints. See the "Lineage" section of this record for full methodology.
-

This record provides an overview of the NESP Marine and Coastal Hub Research Plan 2023 project "Assessing changes in black rockcod abundance and size". For specific data outputs from this project, please see child records associated with this metadata. -------------------- The Black Rockcod (Epinephelus daemelii) is a large, reef-dwelling species that can live for more than 60 years. In Australia it occurs along the coast of New South Wales, including at Lord Howe Island. Black Rockcod populations have been significantly reduced here due to overfishing, accidental hooking, and loss or degradation of estuarine and intertidal nursery habitats. As a result, the species is listed as Vulnerable under Commonwealth and NSW legislation. Despite having been protected from fishing in NSW since 1983, Black Rockcod are still taken illegally, or caught incidentally and released, which can lead to mortality post-release from embolism. Long-term population monitoring is a high priority identified by the species’ recovery plan and the NSW Fisheries Scientific Committee. In 2010, a broadscale baseline survey (81 sites) was undertaken in northern NSW and Lord Howe Island, followed by smaller surveys every four to five years. This project repeated the initial 81 baseline site surveys to assess if protection measures, such as marine protected area sanctuary zones, are assisting in recovery of black rockcod. This contributed to a 13-year time series (2010 – 2023) that was used to examine distribution and population structure of rockcod to assess if recovery actions being implemented are effective. Outputs • underwater visual census (UVC) data for black rock cod [dataset] • Final project report [written]
-
Benthic habitat annotations of stereo Baited Remote Underwater Video (Stereo-BRUV) and panoramic drop camera imagery, were completed as part of a report funded by the NESP Marine & Coastal Hub. This report focussed on an IUCN II zone in the South-west Corner Marine Park off the 'Capes region' near Margaret River. These data were analysed in TransectMeasure using a modified version of the CATAMI scheme.
-
The Black Rockcod (Epinephelus daemelii) is a large, slow-growing, long-lived reef fish that occurs in Australia along the coast of New South Wales, including at Lord Howe Island. Populations of black rockcod have been significantly reduced here due to overfishing, accidental hooking, and loss or degradation of estuarine and intertidal nursery habitats. As a result, the species is listed as ‘Vulnerable’ under both the Commonwealth Environmental Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 and the NSW Fisheries Management Act 1994. Despite having been protected from fishing in NSW since 1983, black rockcod are still taken illegally, or caught incidentally and released, which can lead to mortality post-release from embolism. Its protection status results from concerns of population declines across its range. The NSW Government has identified long-term population monitoring as a a high priority for the species’ recovery plan. Broadscale surveys of black rockcod were first conducted using the diver Underwater Visual Census (UVC) technique in 2009-11 when 83 sites were sampled from Port Stephens to Cook Island in far northern NSW, including the waters of Lord Howe Island. This NESP Marine and Coastal Hub project 3.14 funded the repeat of these broadscale surveys in 2023, with 8 additional sites (91 total) sampled using the same technique. For each black rockcod sighting, the length of the fish was visually estimated by divers, and also filmed using a diver stereo camera system where possible to obtain an exact length measurement. Other attributes recorded included the habitat the fish was found in, if the sighting was cryptic (i.e. hidden or camouflaged), and the depth of the sighting. Based on the broadscale survey sites in 2009-11, a subset of 19 key Black rockcod survey sites along mainland NSW were established These comprised of two sites in the Cape Byron Marine Park (CBMP), five sites in the Solitary Islands Marine Park (SIMP) two sites at SW Rocks (Fish Rock), and ten sites within the Port Stephens-Great Lakes Marine Park (PSGLMP). An additional 18 key sites were established at Lord Howe Island (LHIMP) and surveyed in 2011, 2019, 2023 & 2024. These surveys involved an identical methodology to the broadscale surveys, but without the use of stereo cameras as diver estimates of fish size were shown to be reasonably similar. This NESP MaC Hub project 3.14 provided funding for the resurveying of the 37 total key sites (where weather permitted) in both 2023 and 2024. The data provided by this record includes: (1) all black rockcod sightings and measurements for broadscale sites (2023) and key sites (2023 & 2024); (2) a comparison of the counts of black rockcod recorded at broadscale sites in 2009-11 (n=83) and again in 2023 (n=91); and (3) a comparison of the count of black rockcod recorded at key monitoring sites in northern NSW (n=19) and Lord Howe Island (n=18) across monitoring years 2009-2024.
-
Tidal wetlands are vulnerable to accelerated rates of sea-level rise projected by climate models. Assessing the resilience, or vulnerability, of these environments requires measurements of rates of vertical accretion, subsidence and elevation gain across a range of coastal settings. The Surface Elevation Table (SET) technique is applied globally to assess the extent of vertical adjustment of tidal wetlands to sea-level rise over decadal timescales. This enables measurement of whether wetlands are keeping pace with sea level rise (measured at tide gauges), or subsiding relative to local sea level rise and thus vulnerable to permanent inundation and loss. Australia’s network of Surface Elevation Tables is one of the most extensive in the world, consisting of over 200 benchmark monitoring stations from Westernport Bay, Victoria to Darwin Harbour, NT. This record describes the consolidated SET data collated from the Australian network (OzSET) as at 2022. This data can be used for analysing change to the elevation of wetlands wetlands at the study sites encompassed by OzSET.
-
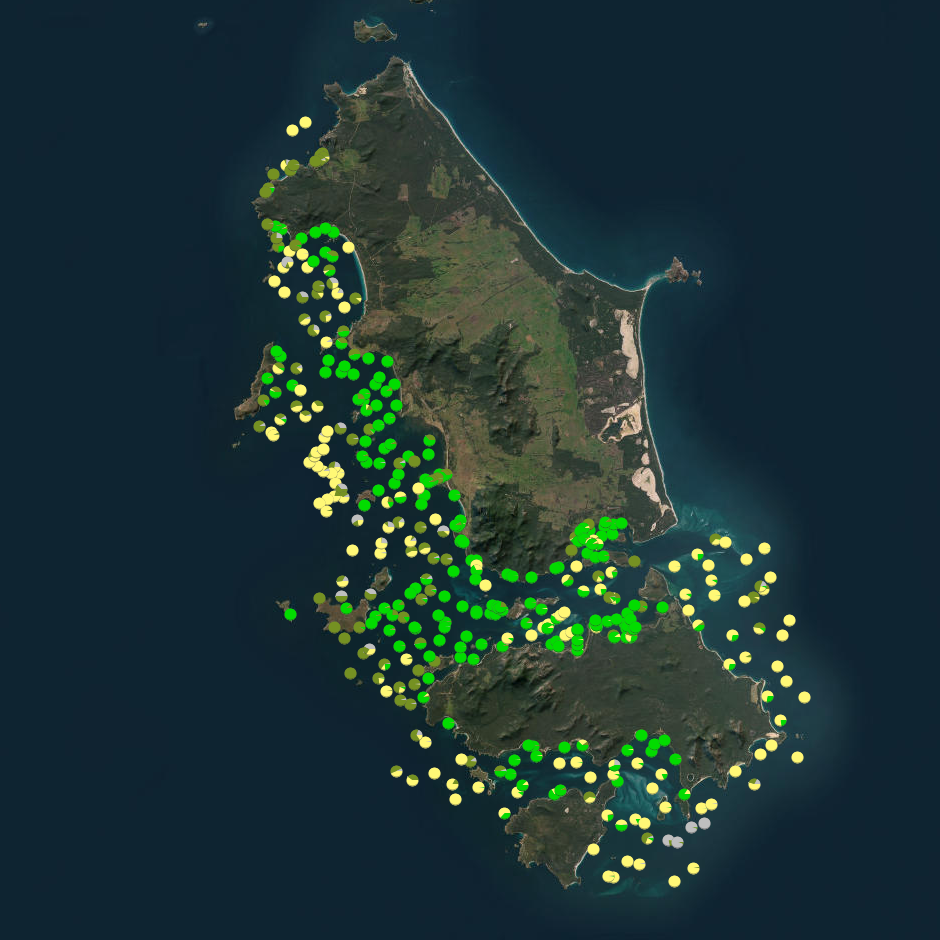
Seagrass beds are a dominant marine ecosystem of Tayaritja (the Furneaux Group of Islands) in the north-eastern waters off Tasmania. Historical coarse mapping has indicated extensive beds of Posidonia, Amphibolis, Heterozostera, and Zostera species, potentially comprising some of the largest and deepest seagrass extents found in temperate Australian waters. However, limited data on the distribution and ecological value of these seagrass habitats represents a significant knowledge gap in understanding Australia's wetland natural assets. This project mapped the extent, ecological composition, population structure, and blue carbon value of seagrass beds around Tayaritja, in partnership with the Tasmanian Aboriginal Centre. The study area focused on the coastal waters surrounding Flinders Island in the western Furneaux Group, with mapping extending from the high tide line to the depth limit of reliable optical detection (approximately 30 m), based on analysis of field data and satellite imagery capabilities in the region. The field validation component of this study involved deployment of benthic video platforms to capture imagery of seagrass beds and associated ecosystems. A field campaign deployed a Benthic Observation Survey System (BOSS) and unBaited Remote Underwater stereo-Video system (stereo-uBRUV) at approximately 400 locations to collect photoquadrats and validate remote sensing outputs. Imagery annotation was conducted in the SQUIDLE+ platform. See dataset https://doi.org/10.25959/e4s6-ge74 for habitat maps derived from field validation and remote sensing inputs. The approach developed through this study contributed to the creation of the NESP Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for Seagrass Mapping using Optical Remote Sensing (https://sustainabledevelopmentreform.github.io/nesp-sop-seagrass-mapping).. See the "Lineage" section of this record for full methodology of field collection techniques.
-

This record provides an overview of the NESP Marine and Coastal Hub scoping study - "Research needs for assessment and monitoring of nutrients, chemicals and antimicrobials in the marine environment". No data outputs were generated by this project. -------------------- Coastal water quality is threatened by an increasing volume of chemicals produced and used in our modern lives. These chemicals are commonly incorporated into pharmaceuticals and household items, and subsequently discharged into coastal areas from a broad range of point sources. Recently emerging contaminants include a variety of chemical (e.g. heavy metals, pharmaceuticals, pesticides, nutrients) and microbiological (e.g. pathogens, antibiotic resistant microbes) sources that are discharged in sewage, stormwater, estuarine flows and industrial wastes. For many of these chemicals, our understanding of their environmental concentrations and biological effects is limited. When new scientific information emerges to suggest that a particular contaminant may be hazardous, this is refered to as a contaminant of emerging concern (CEC). There is limited data about the environmental occurrence and biological effects of CECs, but emerging research suggests they have the capacity to be toxic. With an increasing list of CECs detected in the environment, important questions remain unanswered around which contaminants and scientific knowledge gaps should be prioritised. This desktop study engaged CEC stakeholders from academic research, government, water utilities, and non-government organisations to collaboratively identify priority CEC issues in Australia’s marine ecosystems. The project delivers a risk-based framework for future CEC research directions and water quality management priorities. Outputs • Final Project Report [written]
 IMAS Metadata Catalogue
IMAS Metadata Catalogue