Saturation of oxygen {O2} in the water body [dissolved phase]
Type of resources
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
-
This dataset consist of dissolved oxygen (DO) and temperature data collected using HOBO Dissolved Oxygen loggers (U26-001) under FRDC project 2016-067. Loggers are deployed on strings in two locations in Macquarie Harbour, Tasmania.
-
This dataset consists of data collected by the real-time dissolved oxygen (DO) monitoring system in Macquarie Harbour, Tasmania, originally established under the Sense-T program, continued under FRDC project 2016-067 and deployed and maintained by IMAS. The system consists of 3 strings of acoustically telemetered, optical fluorescence DO, temperature and depth sensors (VEMCO, Bedford, Canada) which measure DO in % saturation, temperature in °C and depth in meters. The dataset spanning the time period from the 1st of January 2017 to the 19th of April 2017 consists of data collected using the first generation of sensors as described above. Subsequent quarterly updates from the 3rd of June 2017 onwards consist of data collected using the new generation of tags which contain a tilt instead of a depth sensor.
-
Conducted under the Coast and Clean Seas program of the Natural Heritage Trust fund, this study provides a summary and assessment of water quality parameters, as indicators of estuarine health, in 22 selected Tasmanian estuaries. The estuaries are: Duck Bay, East Inlet, Black River, Don River, Mersey River, Port Sorell, Boobyalla Inlet, Little Musselroe River, Ansons Bay, Grants Lagoon, Douglas River, Great Swanport, Meredith River, Little Swanport, Earlham Lagoon, Browns River, Cloudy Bay Lagoon, Catamaran River, Cockle Creek, Pieman River, Nelson Bay River and Arthur River (for location, see Fig. 1 in the attached report). Information is summarised on both a State wide and individual estuary basis.
-
This study considered a range of water-column and sediment (benthos) based variables commonly used to monitor estuaries,utilising estuaries on the North-West Coast of Tasmania (Duck, Montagu, Detention, and Black River). These included: salinity, dissolved oxygen, turbidity, nutrient and chlorophyll a levels for the water-column; and sediment redox, organic carbon content, chlorophyll a and macroinvertebrate community structure amongst the benthos. In addition to comparing reference with impacted estuaries, comparisons were also made across seasons, commensurate with seasonal changes in freshwater river input, and between regions within estuaries (upper and lower reaches) - previously identified in Hirst et al. (2005). This design enabled us to examine whether the detection of impacts (i.e. differences between reference and impacted systems) was contingent on the time and location of sampling or independent of these factors. This data includes sampling from Duck River, Montagu River, Detention River, and Black River.
-
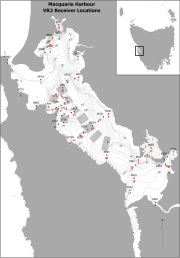
Fixed position oxygen and water temperature logger data from the Macquarie Harbour World Heritage Area (WHA). Two Hobo oxygen data loggers are positioned at approximately 15 m depth at different sites within the WHA, with the intent of monitoring representative mid-bottom water oxygen values in the WHA as these were identified in previous studies to be naturally low due to limited seawater exchange at the harbour entrance, and thus likely to be most susceptible to anthropogenic factors that may increase oxygen demand and alter WHA conservation values. These values include core habitat of the Maugean Skate, a listed threatened species. This work is funded by WHA advisory board via the Nature Conservation Branch of DPIPWE and is part of a larger study being conducted by IMAS undertaking a biological baseline study of the biodiversity of the Macquarie Harbour WHA. This data spans 08/11/14 to present (most recent update 02/02/17).
-

This database contains sampling effort, catch records, biological data, and water quality data for sampling and catches of elasmobranchs in northern Australian rivers, estuaries and coasts undertaken under the National Environmental Research Program (NERP) Marine Biodiversity Hub Project 2.4 'Supporting Management of Listed and Rare Species'. and the National Environmental Science Program (NESP) Marine Biodiversity Hub Project A1 'Northern Australian Hotspots for the Recovery of Threatened Euryhaline Elasmobranchs'. Surveys using gillnets and rod-and-line were undertaken in the Top End region of the Northern Territory and the Kimberley region of Western Australia. Selected animals were tagged for movement ecology, habitat use and mortality estimates (acoustic telemetry), and tissue samples were collected from all fish for molecular analyses (population genetics and close-kin mark-recapture).
-
Water temperature, averaged across the water column, in Storm Bay followed a distinct seasonal cycle each year, reaching a low of 9 °C and a high of ~ 19 °C. Warmest temperatures were in February, followed by a gradual cooling throughout autumn to a winter minimum in August, then increasing again during spring. Across the sites, the median temperature varied little, with site 3, the most marine of the sites, showing the least spread in values. Median salinity varied little across Storm Bay, being slightly higher at sites 3 and 6, highlighting the marine nature of site 3 and the patterns of seawater circulation in Storm Bay. The lowest salinities were recorded at site 1, where less saline surface waters flow into the bay from the Derwent Estuary. Seasonally, salinity was highest in autumn, with slightly fresher water present in Storm Bay in spring. Some lower salinity values were recorded in July and August, suggesting the presence of less saline subantarctic water flowing into the bay, or freshwater flow from the Derwent. Glider transects show slight lower salinity in summer, then mild stratification in autumn to spring, especially in the shallow regions near the mouth of the Derwent.
-
We implemented a monitoring program developed by Crawford and White (2006), which was designed to assess the current condition of six key estuaries in NW Tasmania: Port Sorell, the Leven, Inglis, Black, Montagu and Arthur River estuaries. This study considered a range of water quality and ecological indictors commonly used to monitor estuaries. These included: salinity, temperature, dissolved oxygen, turbidity, pH, nutrients (nitrate + nitrite, dissolved reactive phosphorus and ammonia), silica molybdate reactive and chlorophyll a for the water column; chlorophyll a and macroinvertebrate community structure amongst the sediments.
-
Indicators of estuarine ecosystem health – temperature, salinity, turbidity, dissolved oxygen, chlorophyll a, pH, nutrients - were sampled each month for twelve months at four sites in Georges Bay and at the bridge at the river mouth by the Tasmanian Aquaculture and Fisheries Institute (TAFI), community volunteers and Break O’Day Council staff. Another indicator, macroinvertebrate fauna, was sampled by TAFI in winter and summer, and data were obtained on pathogen levels from the Tasmanian Shellfish Quality Assurance Program.
 IMAS Metadata Catalogue
IMAS Metadata Catalogue