Sex
Type of resources
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
-
Adult reproductive data for redbait is based on collections taken by midwater trawling during the spawning season and includes the biological information - size, sex, reproductive condition (weight and stage). Histological examination of mature ovaries provides information on spawing activity and preserved gonads are examined to determine batch fecundity.
-
Between January and March 2003, 25 (15 females, 9 males, 1 no sex recorded) draughtboard sharks, sourced from the Crayfish Point Reserve and the east coast of Tasmania (42-43°S, 147-148°E), were fitted with the acoustic transmitters to investigate movement behaviour.
-
The southern calamari acoustic telemetry data-set includes information on the tagging and tracking of southern calamari on the east coast of Tasmania. The information includes biological information of tagged squid, deployment information of acoustic receivers and tracking data of squid movement.
-
In Tasmania, SCUBA surveys of seahorses populations were conducted. Intensive surveys were conducted in 2000 to 2004 in the Derwent River around Hobart (submonthly & then monthly) and twice yearly surveys from 2004/5 on east coast and Derwent River, until 2007. Mark-recapture studies were done to estimate population size, and life history parameters.
-
SCUBA surveys and mark-recapture of seahorse populations in Sydney Harbour using visible implant fluorescent elastomer.
-
Between January 2000 and January 2007, sharks were tagged during routine fishery dependent and independent rock lobster catch sampling trips around southwestern and eastern Tasmania and in the Crayfish Point Reserve. For each shark, sex, total length and clasper length (males) were recorded.
-
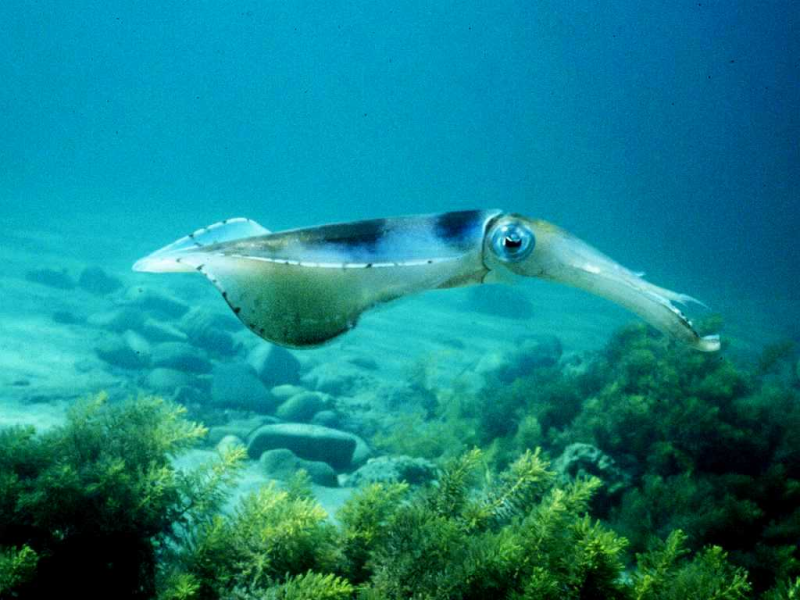

The southern calamari data-set includes all biological data (including length, weight, sex, maturity stage, egg size, and some age information) for southern calamari collected primarily from the east and southeast coasts of Tasmania.
-
Sampling of commercial mid-water trawl catches for small pelagics from waters adjacent to Tasmania have yielded an extensive biological dataset in space and time. As a minimum, size composition information is available from most commerical shots undertaken between 2002 and 2006, referenced with operational information (location, depth and catch weight). Subsamples of the key small pelagics, redbait, jack mackerel and blue mackerel, were examined for size, sex, gonad weight and stage and otoliths have been retained for age determination. Further data has been collected since the initial investigation.
-
Targeted trace elemental analysis was used to investigate the population structure and dispersal patterns of the holobenthic octopus species Octopus pallidus. Multi-elemental signatures within the pre-hatch region of the stylet (an internal ‘shell’) were used to determine the common origins and levels of connectivity of individuals collected from 5 locations in Tasmania. To determine whether hatchling elemental signatures could be used as tags for natal origin, hatchling stylets from 3 of the 5 locations were also analysed.
-
Characterisation of lobster (Jasus edwardsii) abundance and change in abundance at three different sampling sites (Cape Paul Lemanon, North Bay and Fortescue Bay) on the south-east coast of Tasmania, was assessed by GPS tracked SCUBA diver swims of 60 minutes in length whereby GPS was logged approximately every 5 seconds. Large tagged Rock Lobsters were introduced into one of the sampling sites, North Bay (which was closed to fishing). The swims are also being used to assess the impact of reef closure on the local lobster population.
 IMAS Metadata Catalogue
IMAS Metadata Catalogue