IMAS Data Manager
Type of resources
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
-
Data to accompany publication on wild diet of southern rock lobster on the east coast of Tasmania. In this study we collected 64 lobsters and analysed the diet of each individual using stomach contents, stable isotope analysis and DNA identification of prey species in faecal samples.
-

Locations of the Oysters Tasmania's Sensor Network. The sensor network provides real-time data on salinity, water temperature, and depth in shellfish growing areas in Tasmania. Oyster growers can access the sensor data via the ‘ShellPOINT’ portal (https://www.oysterstasmania.org/shellpoint.html).
-
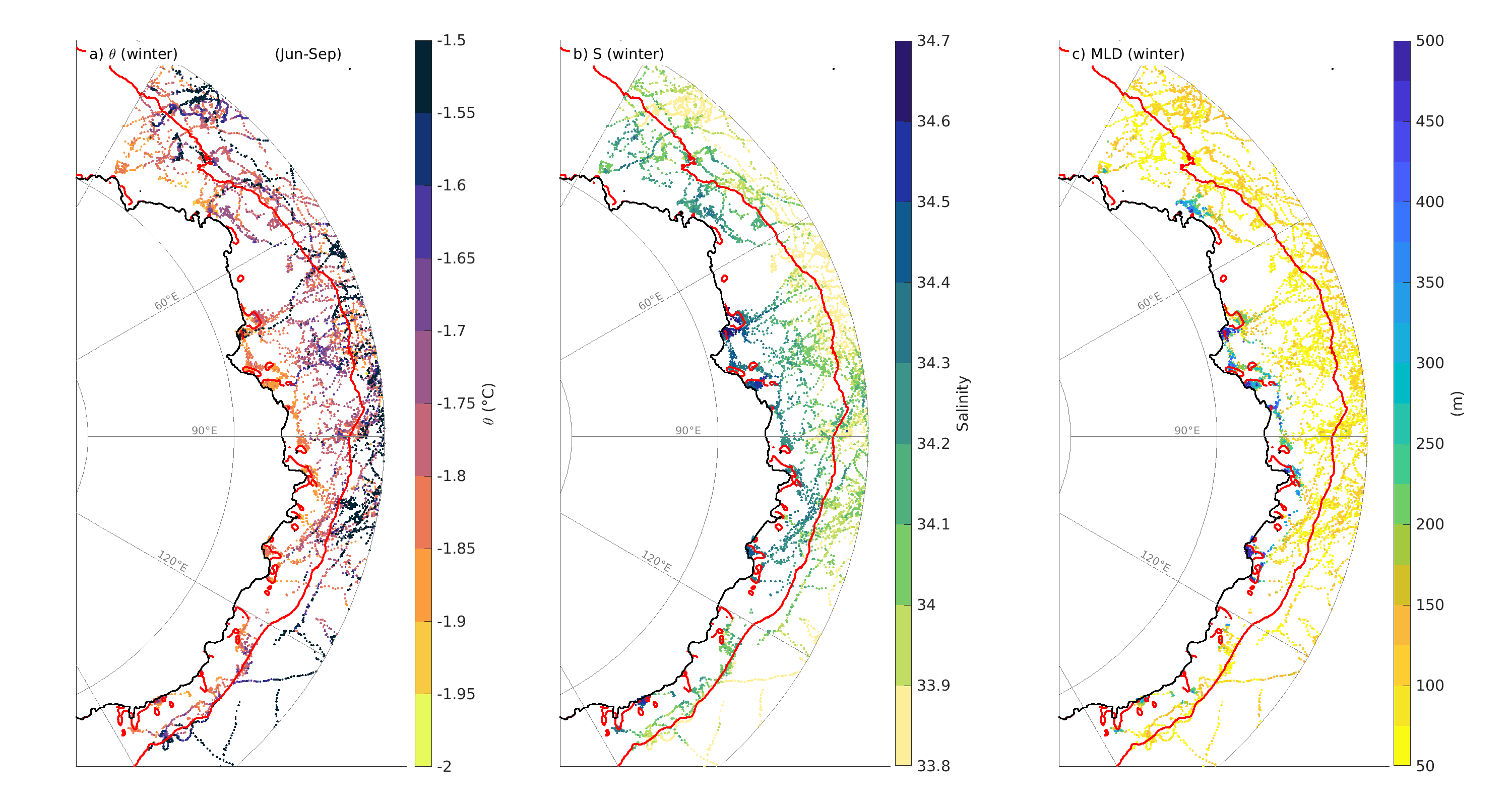
This is a collection of data in East Antarctica from Southern Elephant seal's between 2004 and 2009. The monthly data set has been further classified by polynya and year. Additionally, we provide a dataset of the polynyas contours defined following a criteria of 75% of sea-ice concentration for each individual month between 2004 and 2019. Data are provided in .mat format
-

This dataset contains the general location of five restoration projects around Tasmania: Angasi oyster (Ostrea andasi), Giant Kelp (Macrocystis pyrifira), seagrass habitat (using Environmentally Friendly Moorings), saltmarsh fish habitat, and wetland restoration. The locations don't present the exact restoration sites.
-

This dataset depicts the location of the Broadscale Environmental Monitoring Program (BEMP) sites. It was compiled from data provided by EPA Tasmania, IMAS and published reports. BEMP was initiated in 2009 by the State Government to provide knowledge and information on ecosystem function in the D’Entrecasteaux Channel and Huon Estuary. BEMPs have been developed for all marine farming regions. The objective of each program is to document (on an ongoing basis) broadscale spatial and temporal trends for key environmental parameters, allowing assessment of the environmental effects of finfish aquaculture in Tasmania. Marine farming licence conditions include participation in respective BEMPs. The BEMP program initially covered assessment of water column and sediment health at a broadscale level but has been expanded to include inshore reef, deep-reef and seagrass distribution and health. Seagrass monitoring occurs over transects. In this dataset, only the start location is displayed. Sediment sampling includes benthic infauna, stable isotopes, particle size, visual assessment, redox analysis, and sulphide measurements. Visual assessment, redox and sulphide analysis is carried out each year, while analysis of benthic infauna, stable isotopes and particle size is undertaken every four years. In the intervening years these samples are collected, preserved and retained. Water quality analytes include physico-chemical parameters (temperature, dissolved oxygen and salinity), nutrients (dissolved nutrients: ammonia, nitrate, phosphate, and silicate, nutrients: total nitrogen, total phosphorous), chlorophyll a and phytoplankton species counts. Water quality sampling is undertaken monthly from May to January and fortnightly from February to April.
-
Southern Rock Lobster (Jasus edwardsii) commercial fishery catch by block (in tonnes) and nominal Catch Per Unit Effort (CPUE, in kg/pot lift) per lobster fishing block per year for all depths. The data was retrieved from the Tasmanian Wild Fisheries Assessments site (https://tasfisheriesresearch.org/). Tasmanian wild fisheries stock assessments are conducted by the Fisheries and Aquaculture Centre of the Institute of Marine and Antarctic Studies (IMAS) on behalf of the Tasmanian Department of Natural Resources and Environment (NRE Tas). Under the Sustainable Marine Research Collaboration Agreement (SMRCA), IMAS conduct fishery assessments, provide expert management advice and undertake scientific research on Tasmanian fisheries issues for NRE Tas.
-
This submission creates a static snapshot of data from the Autonomous Underwater Vehicle (AUV) and stereo-BRUV annotation data from the National Environmental Science Program (NESP) Elizabeth and Middleton Reef survey. More details on the survey can be found at https://www.nespmarine.edu.au/document/elizabeth-and-middleton-reefs-lord-howe-marine-park-post-survey-report.
-
Data pertain to analysis of GRACE time series of mass change in both gridded and basin format. The GRACE data are based on the COST-G solution obtained from http://gravis.gfz-potsdam.de/home. Both 50km regular gridded data and basin-level time series are included, as well as the SAM and ENSO climate indices on which the regressions were based. The gridded datasets provided here include derived quantities from the regressions such as trends, uncertainties, and regression coefficients in NetCDF format.
-
At the inception of our project, no study had examined particle fluxes in the Subantarctic Zone (SAZ) of the Southern Ocean, despite the fact that the SAZ represents a large portion of the total area of the Southern Ocean, serve as a strong sink for atmospheric (~1G t C yr-1 [Metzl et al., 1999]), and is central to hypotheses linking particle fluxes and climate change [Francois et al., 1997; Kumar et al., 1995; Sigman et al., 1999]. The SAZ serves as an interface between the cold nutrient-rich waters to its south and the nutrient-depleted subtropical gyres to its north. SAZ upper layers are marked by a thick layer of relatively homogenous Subantarctic Mode Water (SAMW), which overlies Antarctic Intermediate Water (AAIW). Both water masses are subducted northward beneath the subtropical gyres. Thus particles leaving the surface in these regions contribute to carbon redistribution via both the fraction that reaches the deep sea by settling and the fraction that is remineralized within SAMW or AAIW and subsequently subducted. The SAZ exhibits surface water carbon dioxide partial pressures well below atmospheric equilibrium, but PFZ waters are closer to atmospheric equilibrium in this sector [Metal et al., 1999; Poppet al., 1999]. The relative physical and biological contributions to these carbon dioxide partial pressure variations are unclear, but it is important to determine them because physical and biological carbon dioxide transfers are expected to show different responses to climate change [ Matear et al., 1999; Sarmiento and LeQuere, 1996]. For these reasons we focused on the SAZ and, for comparative purposes, on the PFZ to its south. We measured particle fluxes using moored sinking particle traps at three sites in the SAZ, in the PFZ, and beneath the Subantarctic Front (SAF), which separates them. This record describes particle flux data collected between 2000 and 2001. The NetCDF data contains the following variables. Please note not all variables are supplied in all files, specifically there are not uncertainty estimates and no quality control flags for this data. -----DATA DICTIONARY----- Name, description, units, standard name TIME, time, YYYY-MM-DD, time of sample midpoint TIME_START, time sample open, YYYY-MM-DD, time sample open NOMINAL_DEPTH, depth, m, nominal depth LATITUDE, latitude, degrees_north, latitude of anchor LONGITUDE, longitude, degrees_east, longitude of anchor pressure_actual, actual, dbar, actual pressure sample, sample number, 1, sample number sample_quality_control, quality flag for sample number, unitless, quality flag for sample number mass_flux, <1mm, mg m-2 d-1, particulate total mass flux mass_flux_uncertainty, uncertainty for particulate total mass flux, mg m-2 d-1,), uncertainty for particulate total mass flux mass_flux_quality_control, quality flag for particulate total mass flux, unitless, quality flag for particulate total mass flux SAL_BRINE, supernatant, 1, sample supernatant practical salinity SAL_BRINE_uncertainty, uncertainty for sample supernatant practical salinity, 1, uncertainty for sample supernatant practical salinity SAL_BRINE_quality_control, quality flag for sample supernatant practical salinity, unitless, quality flag for sample supernatant practical salinity pH_BRINE, supernatant, 1, sample supernatant pH NBS scale pH_BRINE_uncertainty, uncertainty for sample supernatant pH NBS scale, 1, uncertainty for sample supernatant pH NBS scale pH_BRINE_quality_control, quality flag for sample supernatant pH NBS scale, unitless, quality flag for sample supernatant pH NBS scale PC_mass_flux, <1mm, mg m-2 d-1, particulate total carbon mass flux PC_mass_flux_uncertainty, uncertainty for particulate total carbon mass flux, mg m-2 d-1, uncertainty for particulate total carbon mass flux PC_mass_flux_quality_control, quality flag for particulate total carbon mass flux, unitless, quality flag for particulate total carbon mass flux PN_mass_flux, <1mm, mg m-2 d-1, particulate total nitrogen mass flux PN_mass_flux_uncertainty, uncertainty for particulate total nitrogen mass flux, mg m-2 d-1, uncertainty for particulate total nitrogen mass flux PN_mass_flux_quality_control, quality flag for particulate total nitrogen mass flux, unitless, quality flag for particulate total nitrogen mass flux POC_mass_flux, <1mm, mg m-2 d-1, particulate organic carbon mass flux POC_mass_flux_uncertainty, uncertainty for particulate organic carbon mass flux, mg m-2 d-1, uncertainty for particulate organic carbon mass flux POC_mass_flux_quality_control, quality flag for particulate organic carbon mass flux, unitless, quality flag for particulate organic carbon mass flux PIC_mass_flux, <1mm, mg m-2 d-1, particulate inorganic carbon mass flux PIC_mass_flux_uncertainty, uncertainty for particulate inorganic carbon mass flux, mg m-2 d-1, uncertainty for particulate inorganic carbon mass flux PIC_mass_flux_quality_control, quality flag for particulate inorganic carbon mass flux, unitless, quality flag for particulate inorganic carbon mass flux BSi_mass_flux, <1mm, mg m-2 d-1, particulate biogenic silicon mass flux BSi_mass_flux_uncertainty, uncertainty for particulate biogenic silicon mass flux, mg m-2 d-1, uncertainty for particulate biogenic silicon mass flux BSi_mass_flux_quality_control, quality flag for particulate biogenic silicon mass flux, unitless, quality flag for particulate biogenic silicon mass flux TIME_END, time sample closed, YYYY-MM-DD, time sample closed Reference, citable reference DOI, DOI
-
This record presents data used in the paper 'Controls on polar Southern Ocean deep chlorophyll maxima: viewpoints from multiple observational platforms,' Philip W Boyd 𝘦𝘵. 𝘢𝘭., submitted to Global Biogeochemical Cycles, November 2023. All methods for the following datasets are detailed and cross-referenced in the paper. Data were collected from a range of methods, including: • vertical profiles (from 1 m resolved profiling using sensors on a CTD rosette: temperature, salinity, chlorophyll fluorescence, transmissivity - all calibrated) • vertical profiles (from discrete samples collected from CTD rosette or trace metal clean rosette, for nutrients, chlorophyll, POC, dissolved and particulate iron, active fluorescence, net primary productivity, biological iron uptake) • tow-body sections (undulating tow body (Triaxus) for temperature, salinity, chlorophyll fluorescence, transmissivity (and the ratio of chlorophyll fluorescence, transmissivity) • time-series observations from a robotic profiling float (BGC-ARGO) for temperature, salinity, chlorophyll fluorescence, and transmissivity).
 IMAS Metadata Catalogue
IMAS Metadata Catalogue