Pygmy blue whale
Type of resources
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
-
Long-term passive acoustic observations were made at the edge of the continental shelf south of Bremer Bay, Western Australia, from February 2015 to February 2016, in order to assess seasonal patterns in the presence of various baleen and toothed whales around the Bremer Canyon/Marine Park. Further information is available in: Gavrilov A, Erbe C. 2017. Assessment of marine megafauna found at the edge of the continental shelf off Bremer Bay using passive acoustic observations. Report to the National Environmental Science Programme Marine Biodiversity Hub (CMST 2017-3), 35 p. For queries relating to access to raw acoustic files contact the Point of Contact listed in this record.
-
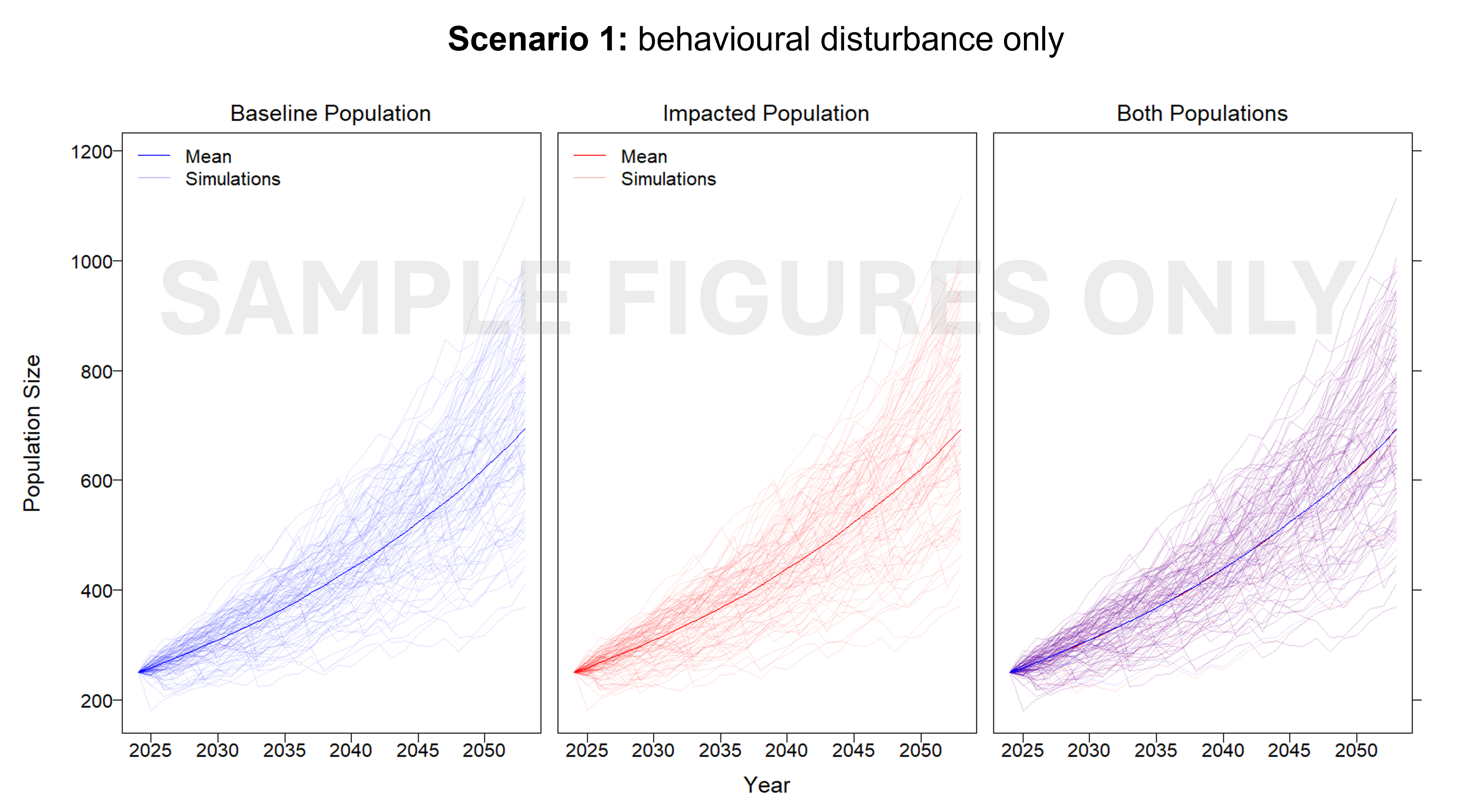
This project developed an interim Population Consequence of Disturbance (iPCoD) model for blue whales (Balaenoptera musculus) and southern right whales (Eubalaena australis) to document a methodology for assessing population-level impacts of one, or multiple, wind farm developments off the southern Australian coast. The iPCoD model was developed in Europe to quantify how disturbances of individuals caused by physiological injury or changes in behaviour can have population-level consequences in data poor marine mammal populations. This model was adapted to suit Australian marine mammal species, highlighting key data gaps for locally threatened populations that overlap in range with the declared offshore wind areas in Australia. Due to the lack of baseline data currently available, this study documented a framework that can be updated as more information becomes available. We outlined how to leverage simulation-based population modelling as a tool for policymakers, industry and management authorities, to aid in environmental impact assessments, with a specific focus on data poor marine mammal populations.
 IMAS Metadata Catalogue
IMAS Metadata Catalogue