Countries | Countries | Australia
Type of resources
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
-
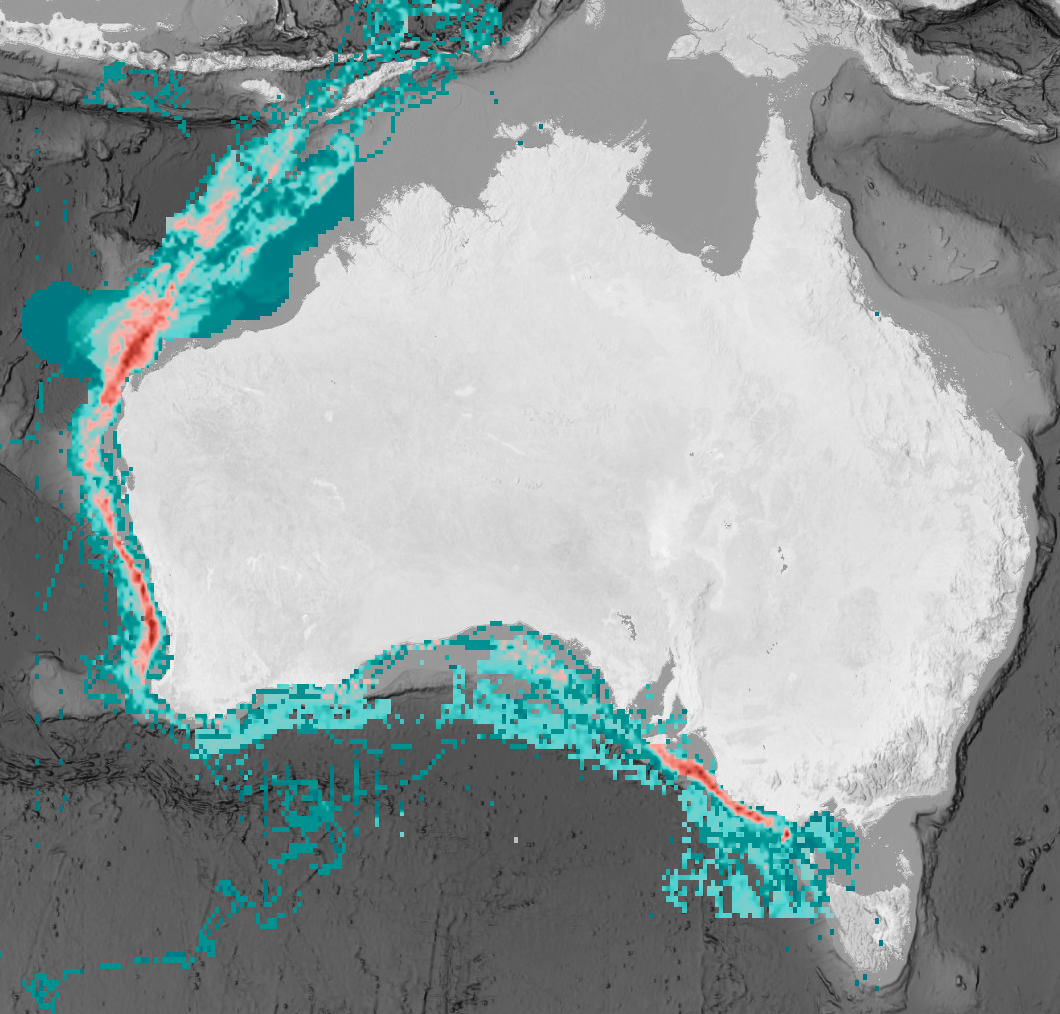
The offshore renewable energy (ORE) sector is rapidly developing in Australian waters to meet the country’s carbon emission targets. However, new developments in the marine environment pose added risk to threatened species. The Eastern Indian Ocean pygmy blue whale (Balaenoptera musculus brevicauda) was identified as a key species by the Australian Government for understanding the potential impacts of ORE developments. This subspecies ranges from the Subtropical Convergence (~40-45°S) to Southeast Asia (~2°S) with most of its documented distribution within the Australia Exclusive Economic Zone. Pygmy blue whale distribution overlaps various anthropogenic activities across their range, which suggests that some level of exposure to pressure and threats is likely. We compiled all available spatial data to quantify the full and foraging distribution of pygmy blue whales and quantified exposure to individual and cumulative threats across the species distribution. Threat exposure analysis included expert elicitation to gather expert input on the probability of exposure to a threat occurring from the spatial overlap between pygmy blue whale distribution and anthropogenic pressures, with a focus on areas undergoing ORE development. The cumulative exposure assessment indicated a relatively low level of exposure of pygmy blue whales to existing threats within Australian waters, particularly those that occur within declared ORE areas. However, several gaps in data and knowledge were identified that need to be addressed prior to development of the ORE industry. Our results provide a robust baseline that can be directly incorporated by industry and regulators as spatial layers into impact assessments. The study helps inform Government, and proponents of wind farms on the current state of knowledge of pygmy blue whale distribution and exposure to threats in Australian waters for use in decision-making, helping facilitate the sustainable development of the ORE industry in Australia.
-
This submission creates a static snapshot of data from the Autonomous Underwater Vehicle (AUV) and stereo-BRUV annotation data from the National Environmental Science Program (NESP) Elizabeth and Middleton Reef survey. More details on the survey can be found at https://www.nespmarine.edu.au/document/elizabeth-and-middleton-reefs-lord-howe-marine-park-post-survey-report.
-
Diel partitioning of animals within ecological communities is widely acknowledged, yet rarely quantified. Investigation of most ecological patterns and processes involves convenient daylight sampling, with little consideration of the contributions of nocturnal taxa, particularly in marine environments. Here we assess diel partitioning of reef faunal assemblages at a continental scale utilizing paired day and night visual census across 54 shallow tropical and temperate reefs around Australia. Day/night differences were most pronounced in the tropics, with fishes and invertebrates displaying distinct and opposing diel occupancy on coral reefs. Tropical reefs in daytime were occupied primarily by fishes not observed at night (64% of all species sighted across day and night, and 71% of all individuals). By night, substantial emergence of invertebrates not otherwise detected during sunlit hours occurred (56% of all species, and 45% of individuals). Nocturnal emergence of tropical invertebrates corresponded with significant declines in the richness and biomass of predatory and herbivorous diurnal fishes. In contrast, relatively small diel changes in fishes active on temperate reefs corresponded to limited nocturnal emergence of temperate invertebrates. This reduced partitioning may, at least in part, be a result of strong top-down pressures from fishes on invertebrate communities, either by predation or competitive interference. For shallow reefs, the diel cycle triggers distinct emergence and retreat of faunal assemblages and associated trophic patterns and processes, which otherwise go unnoticed during hours of regular scientific monitoring. Improved understanding of reef ecology, and management of reef ecosystems, requires greater consideration of nocturnal interactions. Without explicit sampling of nocturnal patterns and processes, we may be missing up to half of the story when assessing ecological interactions.
-
This metadata catalogue presents a list of the data assets used in the analysis presented in this report: Ogier, E., Sen, S., Smith, D. C., Rust, S., Magnusson, A., Jennings, S., Pethiyagoda, N., Spanou, E. (2025). Impact of COVID-19 on the Australian Seafood Industry: January 2020-June 2021 and beyond. Report prepared as part of FRDC project 2021-042: Impacts of COVID-19 on the Australian Seafood Industry: Extending the assessment to prepare for uncertain futures. Canberra, Australia, Fisheries Research and Development Corporation (FRDC).
 IMAS Metadata Catalogue
IMAS Metadata Catalogue