Coastal Waters (Australia) | Coastal Waters (Australia) | South Australia Coast, SA
Type of resources
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
-
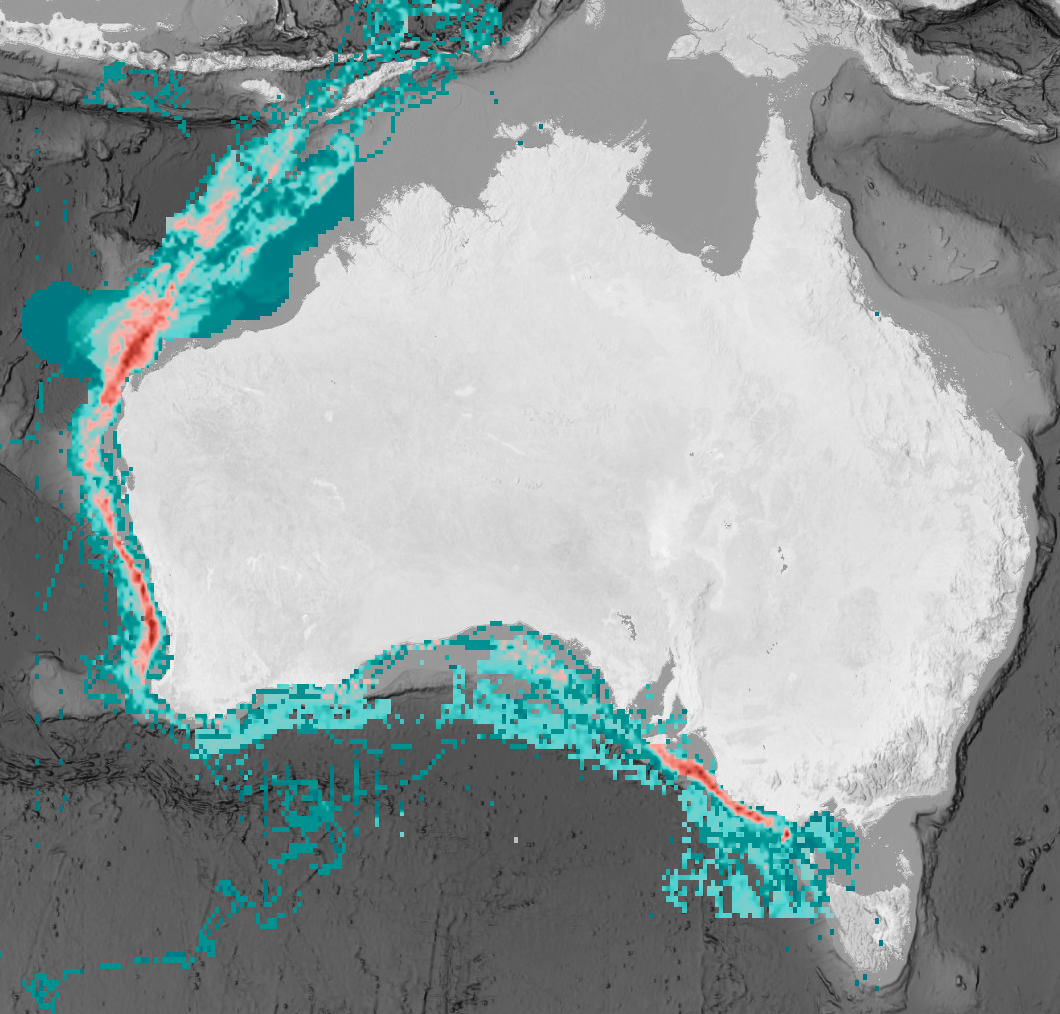
The offshore renewable energy (ORE) sector is rapidly developing in Australian waters to meet the country’s carbon emission targets. However, new developments in the marine environment pose added risk to threatened species. The Eastern Indian Ocean pygmy blue whale (Balaenoptera musculus brevicauda) was identified as a key species by the Australian Government for understanding the potential impacts of ORE developments. This subspecies ranges from the Subtropical Convergence (~40-45°S) to Southeast Asia (~2°S) with most of its documented distribution within the Australia Exclusive Economic Zone. Pygmy blue whale distribution overlaps various anthropogenic activities across their range, which suggests that some level of exposure to pressure and threats is likely. We compiled all available spatial data to quantify the full and foraging distribution of pygmy blue whales and quantified exposure to individual and cumulative threats across the species distribution. Threat exposure analysis included expert elicitation to gather expert input on the probability of exposure to a threat occurring from the spatial overlap between pygmy blue whale distribution and anthropogenic pressures, with a focus on areas undergoing ORE development. The cumulative exposure assessment indicated a relatively low level of exposure of pygmy blue whales to existing threats within Australian waters, particularly those that occur within declared ORE areas. However, several gaps in data and knowledge were identified that need to be addressed prior to development of the ORE industry. Our results provide a robust baseline that can be directly incorporated by industry and regulators as spatial layers into impact assessments. The study helps inform Government, and proponents of wind farms on the current state of knowledge of pygmy blue whale distribution and exposure to threats in Australian waters for use in decision-making, helping facilitate the sustainable development of the ORE industry in Australia.
-

Australia's kelp forests are among the most productive and biodiverse ecosystems on the planet. Giant kelp (Macrocystis pyrifera) can develop extensive forests and create dense surface canopies, providing a variety of ecological functions and ecosystem services including carbon sequestration, nutrient cycling and habitat provision. Giant Kelp forests naturally fluctuate from year to year and experience dramatic interannual variability. However, over the last 4–5 decades, a ~95% loss of surface-canopy forests has been recorded in eastern Tasmania due to a combination of ocean warming, changing currents, recruitment limitation, and intense herbivory by expanding sea urchin populations. While kelp forests also occur on mainland southeastern Australia, relatively little is known about the ecology of Giant Kelp in this region. In recognition of the species' rapid declines in eastern Tasmania and the lack of data elsewhere, Giant Kelp communities in Australia were declared an endangered marine community in August 2012 under the EPBC Act. Given the conservation status of Australian Giant Kelp communities, ongoing threats, and absence of a sanctioned recovery plan, there is an urgent need to establish the current extent for Giant Kelp in Australia, and to monitor changes over time. Historical aerial surveys techniques are costly, logistically difficult, and prone to cloud interference - impairing the ability of resource managers to consistently assess Giant Kelp abundance and distribution across jurisdictions. Recent improvements satellite remote sensing techniques now offer a reliable and cost-effective means for long-term kelp canopy monitoring at broad spatial and temporal scales. This project mapped the surface canopy of Giant Kelp forests from 2016 to 2023 using 3 m resolution satellite imagery across the known historical range in Tasmania, Victoria, southern New South Wales, and eastern South Australia. The mapping workflow was divided into the following broad steps: • Generate a precise land/water mask to exclude intertidal areas • Create a first-pass machine learning (ML) classification using Sentinel-2 (10 m) imagery • Acquire and process PlanetScope (3 m) daily imagery • Train and evaluate a second-pass ML model for kelp detection using PlanetScope imagery • Visualise results via an interactive Earth Engine application to enable input from expert review ---DATA DESCRIPTION--- • KelpWatch_KelpExtent_ALL_shp.zip: binary kelp extent - by year x zone (near-coast & estuary/embayment vs open water) • KelpWatch_KelpProb_ALL.zip: continuous probability of kelp - by year x zone x threshold (low vs high)
-
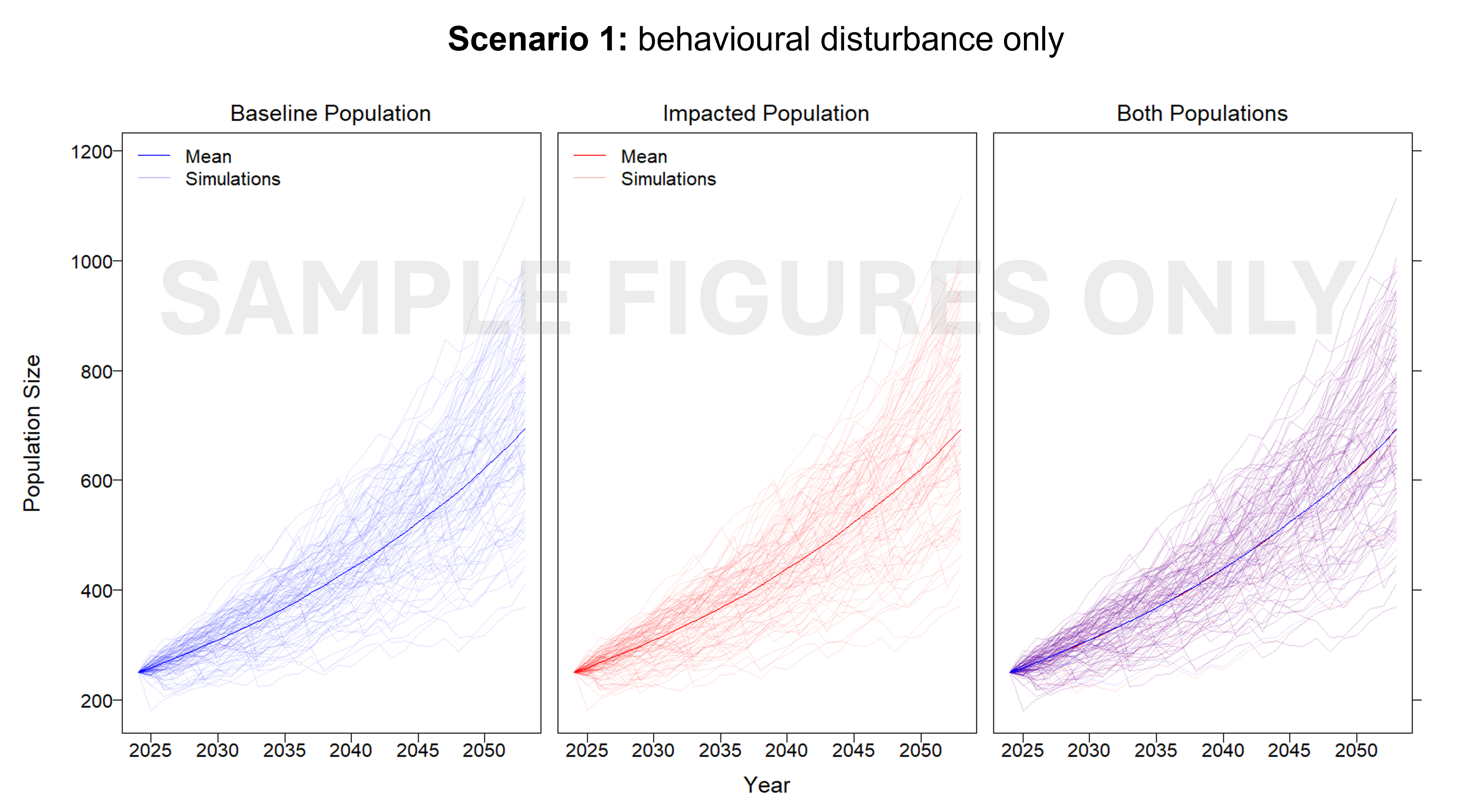
This project developed an interim Population Consequence of Disturbance (iPCoD) model for blue whales (Balaenoptera musculus) and southern right whales (Eubalaena australis) to document a methodology for assessing population-level impacts of one, or multiple, wind farm developments off the southern Australian coast. The iPCoD model was developed in Europe to quantify how disturbances of individuals caused by physiological injury or changes in behaviour can have population-level consequences in data poor marine mammal populations. This model was adapted to suit Australian marine mammal species, highlighting key data gaps for locally threatened populations that overlap in range with the declared offshore wind areas in Australia. Due to the lack of baseline data currently available, this study documented a framework that can be updated as more information becomes available. We outlined how to leverage simulation-based population modelling as a tool for policymakers, industry and management authorities, to aid in environmental impact assessments, with a specific focus on data poor marine mammal populations.
-

This project aimed to identify and map critical habitats for Australian sea lions (Neophoca cinerea) to assess the ecological value of different habitats, and identify risks to their populations. Video imagery, GPS, time-depth and accelerometer/magnetometer data was captured from eight adult female Australian sea lions from Olive Island (n=4) on the western Eyre Peninsula and Seal Bay (n=4) on Kangaroo Island in South Australia. Sea lions were instrumented with animal-borne cameras with integrated accelerometers/magnetometers (CATS Cam, 135 x 96 x 40 mm, 400 g) and satellite-linked GPS loggers with integrated time-depth recorders (SPLASH-10, Wildlife Computers, 100 x 65 x 32 mm, 200 g). Sea lions were sedated and anaesthetised and bio-logging instruments were glued to the pelage on the dorsal midline. Bio-logging instruments were recovered after a single foraging trip (~1-6 days). The data collected in this project provides fundamental information on critical benthic habitats for Australian sea lions, the differences in foraging behaviour of individual sea lions, and their prey preferences. This information improves our understanding of threats to sea lion populations and will support future conservation actions to recover the species.
 IMAS Metadata Catalogue
IMAS Metadata Catalogue