Global / Oceans | Global / Oceans | World
Type of resources
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
-
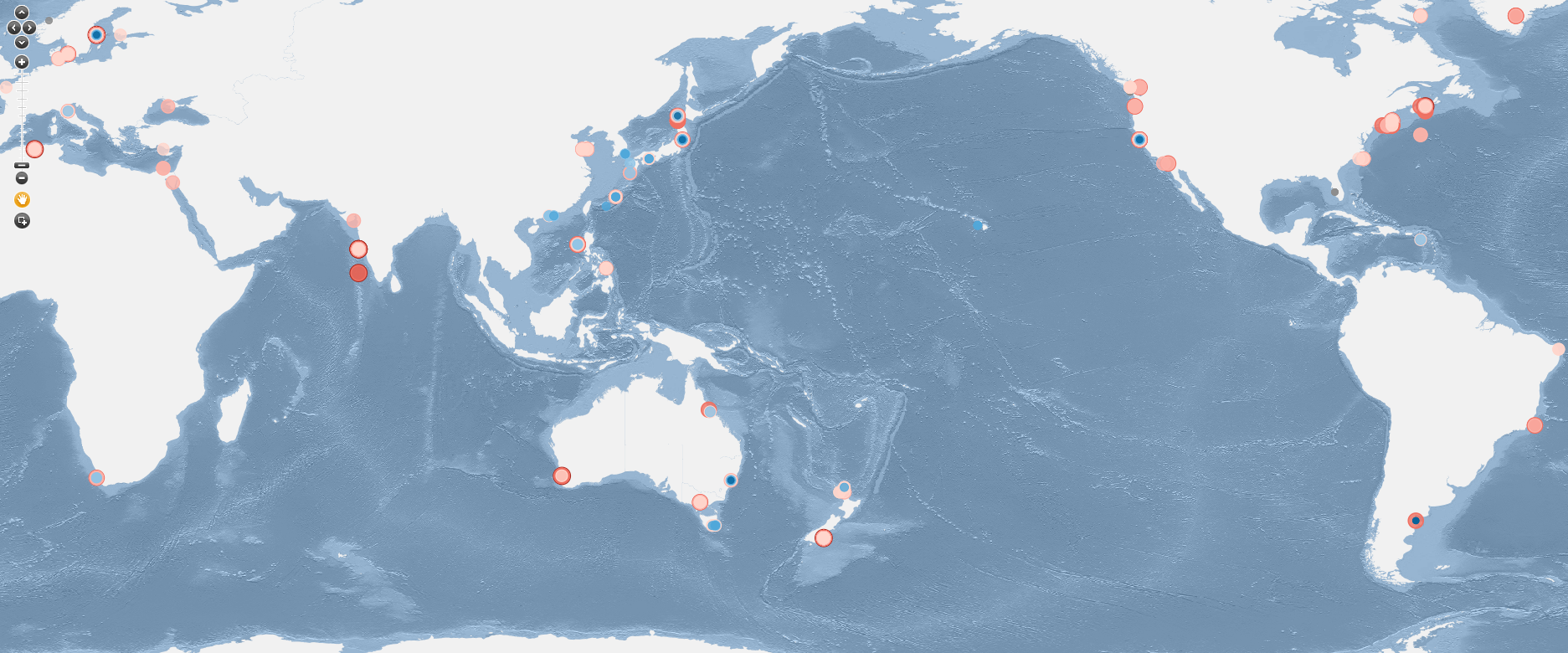
This data was collected and analysed for the project "Dissolved inorganic nitrogen uptake by seaweeds: a global analysis" published in Botanica Marina. Data was compiled between May 2025 and July 2025 from published studies on the uptake kinetics of nitrate (NO₃⁻) and ammonium (NH₄⁺) by marine macroalgae i.e. the rate of Dissolved Inorganic Nitrogen (DIN) uptake rate at a range of DIN concentrations. Each study contained values for the Michaelis-Menten kinetic constants maximum uptake rate (Vmax) and the half saturation constant (Ks), linear uptake gradients, or described biphasic uptake patterns. A total of 84 published studies presenting this data were discovered, with 556 distinct data entries. The project examined DIN uptake rates in marine macroalgae by Phylum, order, experimental irradiance and temperature, geographic location and functional group. Articles were identified through searches on Google Scholar and Web of Science, with all studies reporting Michaelis-Menten kinetic constants or linear uptake slopes included. For each study, we recorded taxonomic information, functional group, the experimental subject (species and algal tissue used), habitat of origin (subtidal, intertidal, or cultured), and season of collection. We also documented experimental conditions, including temperature, irradiance, DIN source (nitrate or ammonium), presence and concentration of other macronutrients (e.g., phosphate or non-target DIN), and the phosphate:DIN ratio of the culture medium. Where available, we extracted kinetic parameters (Vmax, Ks/Km), linear uptake slopes, uptake pattern (saturating, linear, or biphasic), maximum DIN concentration tested, the range of concentrations used in multi-flask experiments, and the time interval over which uptake was measured (for time-course experiments). Geographic coordinates of the study location were also recorded. Each study entry in this dataset includes the full study reference (author and year) and a functional DOI where available (as of November 2025).
-
This atlas uses all of the available full water column profiles of oxygen, salinity and temperature available as part of the World Ocean Atlas released in 2018. Instead of optimal interpolation we use the Data Interpolating Variational Analysis (DIVA) approach to map the available profiles onto 108 depth levels between the surface and 6800 m, covering more than 99% of ocean volume. This 1/2° x 1/2° degree atlas covers the period 1955 to 2018 in 1 year intervals. The DIVA method has significant benefits over traditional optimal interpolation. It allows the explicit inclusion of advection and boundary constraints thus offering improvements in the representations of oxygen, salinity and temperature in regions of strong flow and near coastal boundaries. We demonstrate these benefits of this mapping approach with some examples from this atlas. We can explore the regional and temporal variations of oxygen in the global oceans. Preliminary analyses confirm earlier analyses that the oxygen minimum zone in the eastern Pacific Ocean has expanded and intensified. Oxygen inventory changes between 1970 and 2010 are assessed and compared against prior studies. We find that the full ocean oxygen inventory decreased by 0.84% ± 0.42%. For this period temperature driven solubility changes explain about 21% of the oxygen decline over the full water column, in the upper 100 m solubility changes can explain all of the oxygen decrease, for the 100-600 m depth range it can explain only 29%, 19% between 600 m and 1000 m, and just 11% in the deep ocean.
 IMAS Metadata Catalogue
IMAS Metadata Catalogue